Oxygen-Discovery, Properties, And Applications
Oxygen is a chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group on the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as well as with other compounds. By mass, oxygen is the third-most abundant element in the universe, after hydrogen and helium.

| Property | Value |
| Name | Oxygen |
| Symbol | O |
| Atomic number | 8 |
| Relative atomic mass (Ar) | Colourless as a gas, the liquid is pale blue |
| Standard state | Gas at 298 K |
| Appearance | Group in the periodic table |
| Classification | Non-metallic |
| Block in the periodic table | 16 |
| Group name | Chalcogen |
| Period in periodic table | 2 |
| Period in the periodic table | p |
| Shell structure | 2.6 |
| CAS Registry | 7782-44-7 |
Discovery
Oxygen was discovered independently by Carl Wilhelm Scheele, in Uppsala, in 1773 or earlier, and Joseph Priestley in Wiltshire, in 1774, but Priestley is often given priority because his work was published first.
Physical Properties
Oxygen is a colorless, odorless gas at room temperature. It has a boiling point of -183 degrees Celsius and a melting point of -218.79 degrees Celsius. Oxygen has two allotropes: dioxygen (O2) and ozone (O3).
Chemical Properties
Oxygen is a highly reactive element and forms oxides with almost all elements as well as with other compounds. It is an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements, as well as with other compounds. Oxygen can combine with elements at room temperature and is a component of various compounds such as water, oxides, acids, and organic compounds.
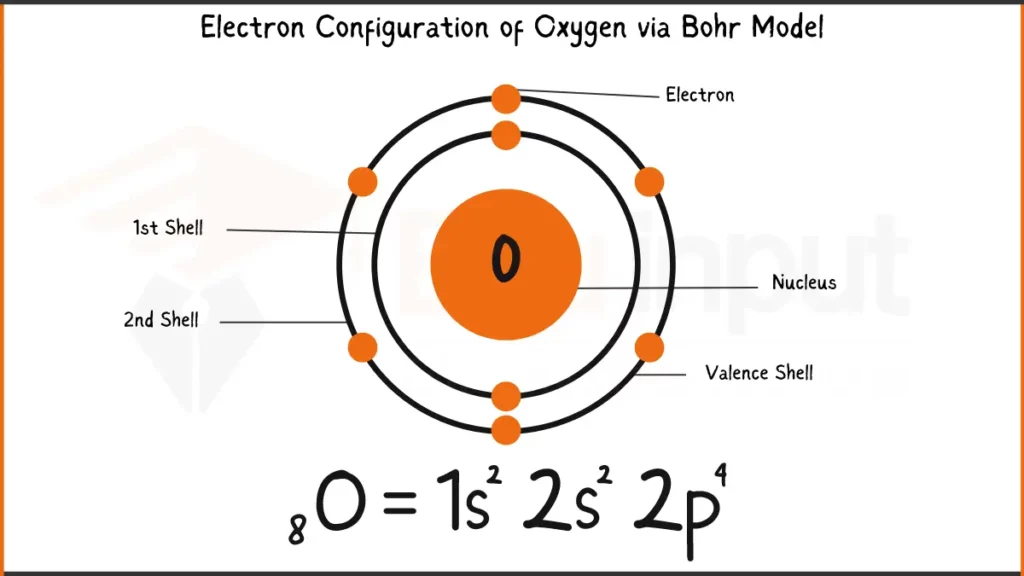
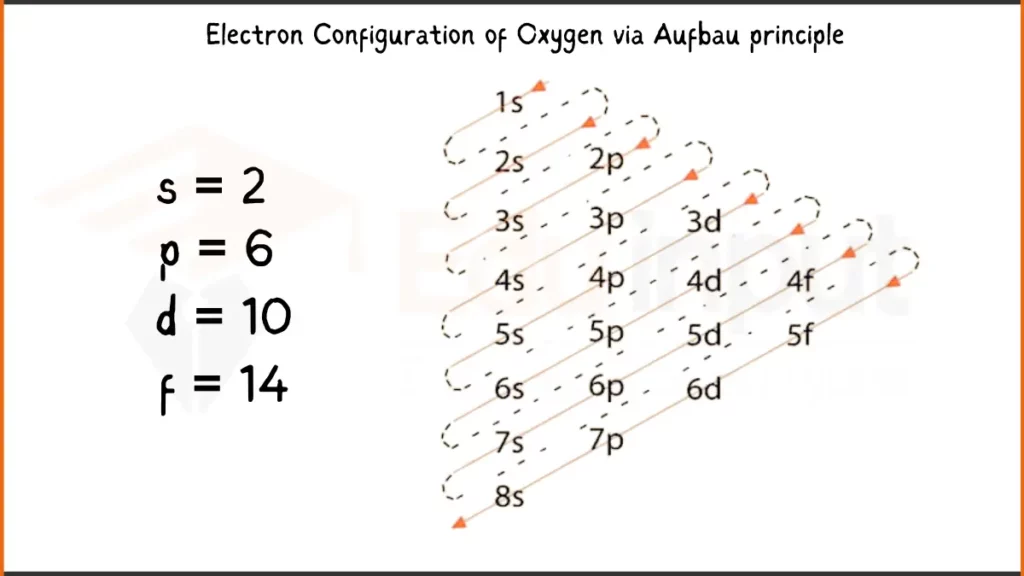
Electronic Configuration of Oxygen
Oxygen (O), essential for life and combustion, has 8 electrons. Its electronic configuration is 1s²2s²2p⁴. This configuration shows 2 electrons each in the first two shells (1s and 2s),4 electrons filling the next shell (2p).
Electronic Configuration of Oxygen via Bohr Model
Electronic Configuration of Oxygen via Aufbau Principle
Facts
- Oxygen makes up about 21% of the Earth’s atmosphere by volume.
- Oxygen is the third most abundant element in the universe.
- Oxygen is essential for the process of respiration in all living organisms.
Applications
Oxygen has many applications in industry, medicine, and other fields. Some common uses of oxygen include:
- Medical oxygen: Oxygen is used in hospitals to treat patients with respiratory distress or hypoxia (low oxygen levels).
- Combustion: Oxygen is used in combustion processes to support combustion and to improve fuel efficiency.
- Welding and metal cutting: Oxygen is used in welding and metal cutting to provide a high-temperature, oxidizing flame.
- Ozone generation: Oxygen is used to generate ozone, which is used for disinfecting water and air.
- Rocket propellants: Oxygen is used as an oxidizer in rocket propellants.







Leave a Reply