Anatomy-History, Types, Scope, And Importance
The description and identification of the structures of living things is a field in the biological sciences, that is being dealt with, under the umbrella of Anatomy. The study of the body of living things goes back more than 2,000 years to the Ancient Greeks. Herophilus is known as the Father of Anatomy.
The word anatomy is derived from the Greek word “anatome,” where “ana” means “up” and “tome” means “cutting. In Ancient Rome, anatomy was originally known as “post mortem analysis.
History of Anatomy
Aristotle wrote about the use of anatomical illustrations, perhaps in connection with the use of animals for medical experimentation.
In the third century BC, the study of anatomy advanced considerably at Alexandria. Many of the discoveries made there can be attributed to Herophilus and Erasistratus, the first to systematically perform human dissections.
For ethical and religious reasons, human dissection was not allowed from the year 150 BC to the year 200 BC. The Hellenistic world had anatomical knowledge about the human body, but it was only found through animal dissections.
In the second century, the famous physician Galen was responsible for the dissection of everything from pigs and monkeys to humans. His findings are often incorrect because the studies could not be confirmed with human corpses.
Galen, however, made his contribution to the study of anatomy but he did not understand the final cause.
“Like cures like” is a well-established principle in both traditional and modern medicine. It’s the basis of many forms of holistic and complementary treatments.
Branches of Anatomy
Anatomy is classified into the following categories:
1. Gross Anatomy
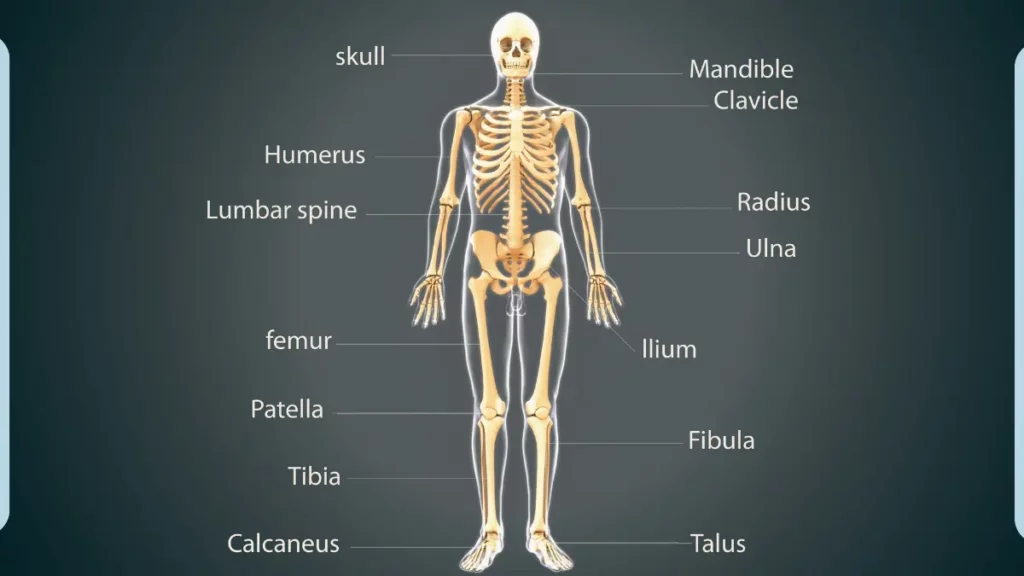
Gross anatomy, also known as macroscopic anatomy, is the study of large structures visible to the naked eye. It is the foundation for all other branches of anatomy and is essential for understanding the overall organization and function of the body.
Gross anatomy is typically divided into two major subdisciplines:
- Systemic anatomy – It focuses on the study of specific organ systems, such as the digestive, respiratory, cardiovascular, and nervous systems.
- Regional anatomy – It focuses on the study of the structures in a particular region of the body, such as the head, chest, or abdomen.
Gross anatomy is studied using methods like:
- Dissection: Dissection involves carefully cutting open an organism to examine its internal structures.
- Imaging techniques: Imaging techniques such as X-rays, MRI, and CT scans can be used to create images of internal structures without having to dissect the body.
- Surface anatomy: Surface anatomy involves the study of the anatomical landmarks and features that can be seen under the skin.
2. Microscopic Anatomy
Microscopic anatomy is also known as histology as it refers to the microscopic study of cells, tissues, and organs.
It uses microscopes to examine the structure and function of these tiny building blocks of the body.
Microscopic anatomy is typically divided into three major subdisciplines:
- Histology: Histology is the study of tissues, which are groups of cells that work together to perform a specific function.
- Cytology: Cytology is the study of cells, the basic units of life.
- Embryology: Embryology is the study of the development of the embryo and fetus from fertilization to birth.
3. Neuroanatomy
Neuroanatomy is the study of the nervous system, which is responsible for controlling all bodily functions. It includes the brain, spinal cord, and nerves.
Neuroanatomy is typically divided into two major subdisciplines:
- Central nervous system anatomy – focuses on the study of the brain and spinal cord.
- Peripheral nervous system anatomy – focuses on the study of the nerves that connect the central nervous system to the rest of the body.
4. Comparative Anatomy
Comparative anatomy is the study of the similarities and differences in the anatomy of different species. It is used to understand how organisms have evolved over time.
Comparative anatomy typically focuses on comparing the anatomy of closely related species, such as humans and chimpanzees. It can also be used to compare the anatomy of organisms from different groups, such as mammals and birds.
5. Embryology
Embryology is a branch of anatomy that studies the process and variations, of how an embryo develops from a single cell into a complete fetus.
6. Zootomy
Zootomy is a branch of anatomy that involves the study of the anatomy of animals. It is the anatomy of animals that compares the structure and function of the animals.
7. Phytotomy
Phytotomy is the study of the internal structure of plants. It is also known as plant anatomy, botany, phytology, or phytotechnology.
Phytotomy originally included plant morphology, but the emphasis has since shifted to the study of plants about their ecology.
8. Human Anatomy
Human Anatomy is the study of the morphology of the human body. It is also known as topographical anatomy, regional anatomy, or anthropotomy.
Scope of Anatomy
There are many jobs available for graduates with a physiology and anatomy degree. Below are some examples of what you can do after your degree in anatomy:
- Lab Technician
- MRI Technologist
- Medical Technologist
- Biomedical engineer
- Research associates
- Pharmacologist
- Physician/ Nurse/surgeon
- Medical Scientist
- Pharmaceutical scientists
- Physical Therapists
- Professor of medicine
Famous Anatomist
- Henry Gray: Known for his book Gray’s Anatomy
- Albrecht Von Haller
- Geoffrey H. Bourne
- Leonardo da Vinci.
- Nicolas Steno.
- Raymond Dart.
- Herbert Jasper.
- Grafton Elliot Smith.
- Albrecht von Haller.
- Giovanni Battista Morgagni
What is studied in anatomy?
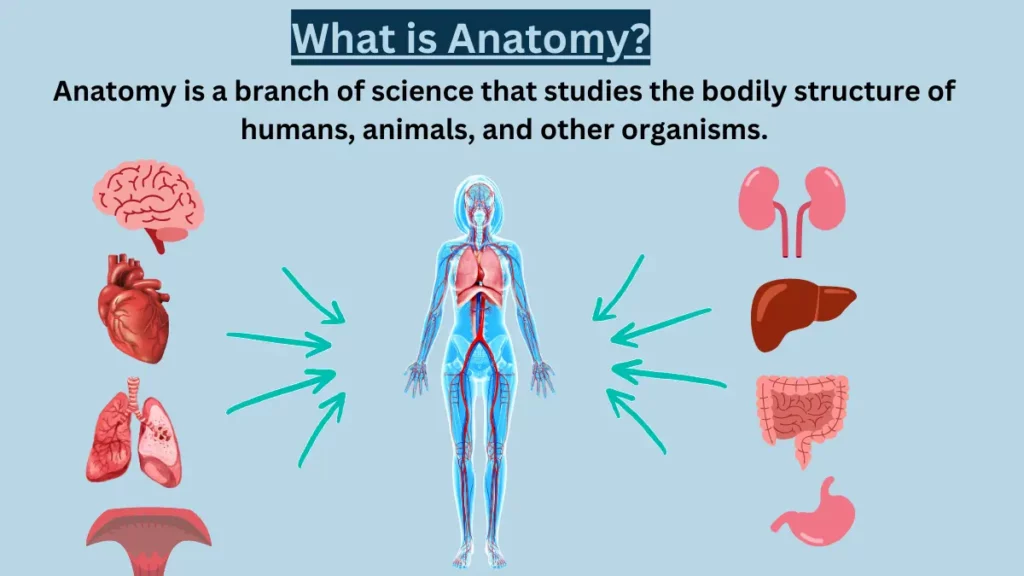
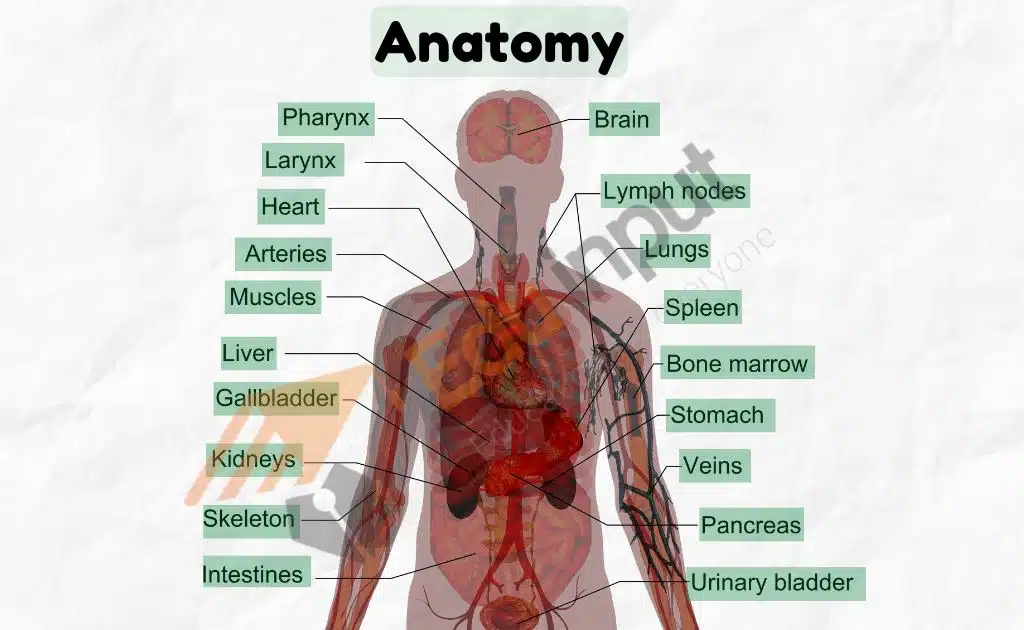
The study of Internal structures of all living organisms, whether they are microscopic or can be seen through the naked eye is associated with Anatomy. It studies the internal structures, their coordination, and their functions in living organisms.
Why is anatomy so important?
Anatomy provides basic knowledge about the body. It helps in understanding the body’s functions.
It can help clear up any concepts that you don’t understand, such as the way our bodies function. A thorough understanding of anatomy and physiology is very important to the success of any career.
What Does An Anatomist Do?
An Anatomist is a specialist in the field of medicine that works to advance medicine. An anatomist works the same as a physician. They work to create better patient care. They work in consumer science, clinical environments, Colleges, or Universities.
You need a PhD in Philosophy if you want to pursue a career as an anatomist. This will give you an idea of the science behind our bodies.
You need to be a board-certified physician to work in clinical settings and you need experience teaching and conducting research in a university setting.
Importance of Anatomy
In the medical field, It’s crucial to have a basic understanding of how the body works at all levels. From what can be seen with the naked eye (gross anatomy) to the molecular level. Knowledge of the body is essential to understand how both structure and function are damaged by disease.
In Anatomy and Physiology, the basics of anatomy and physiology are provided, as well as some topics that are relevant to medical education. It explains the basic principles of how our bodies function.
It is also used in physical education as understanding anatomy and physiology helps a person become a better athlete. Learning about the structure and function of different parts of the body allows a person to achieve a fit and healthy body.
Also Read:
Related FAQs
What is Anatomy?
Anatomy is a branch of Biology, that deals with the description and identification of the structures of living things is a field in the biological sciences.
What are the types of anatomy?
The major types of anatomy include
gross anatomy
microscopic anatomy
human anatomy
phytotomy
zootomy
embryology
What is anthropotomy?
Anthropotomyis the study of the morphology of the human body.
Why is anatomy so important?
In the medical field, It’s crucial to have a basic understanding of how the body works at all levels. From what can be seen with the naked eye (gross anatomy) to the molecular level.
Knowledge of the body is essential to understand how both structure and function are damaged by disease.
What is the difference between anatomy and physiology?
Anatomy and physiology are two of the most basic terms and areas of study in the life sciences. Anatomy refers to the internal and external structures of the body and their physical relationships, and physiology refers to the study of the functions of those structures.
What is the Scope of Anatomy?
There are many jobs available for graduates with a physiology and anatomy degree.
Lab Technician
MRI Technologist
Medical Technologist
Biomedical engineer
Research associates
Pharmacologist
Who is the father of human anatomy?
Herophilus is known as the Father of Anatomy.
Why do we study anatomy?
It can help clear up any concepts that you don’t understand, such as the way our bodies function. A thorough understanding of anatomy and physiology is very important to the success of any career.



Leave a Reply