Female Reproductive System-Anatomy, and Functions
The female reproductive system is the collection of organs and tissues involved in reproduction in females. It has both external and internal parts.
Read What is Reproductive Structure?
The external parts of the female reproductive system include the vulva, labia, clitoris, vaginal opening, and urethral opening.
The internal organs include the vagina, cervix, uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries. These parts work together to enable pregnancy and childbirth.
Also read about: Male Reproductive System
Anatomy of Female Reproductive System
Here are the main parts of female reproductive system:
1. Labia Majora
The labia majora are the outer folds of skin that protect the opening of the vagina. They contain sweat and oil glands and are covered in hair after puberty. The labia majora enclose and protect the other external genital organs.
2. Labia Minora
The labia minora are smaller inner folds of skin located between the labia majora. They surround the openings of the urethra and vagina. The labia minora can vary in size and shape. This tissue is very delicate and can become irritated and swollen.
3. Clitoris
The clitoris is a sensitive protrusion of erectile tissue located at the front of the vulva where the labia minora meet. It contains thousands of nerve endings and is analogous to the penis in males. The clitoris is covered by a fold of skin called the prepuce.
4. Vaginal Opening
The vaginal opening leads to the vagina and allows for menstrual blood flow and childbirth. It is where tampons, fingers, sex toys or penises can enter the vagina.
5. Urethral Opening
The urethral opening is the hole where urine exits the body from the urethra. It is located near the vaginal opening.
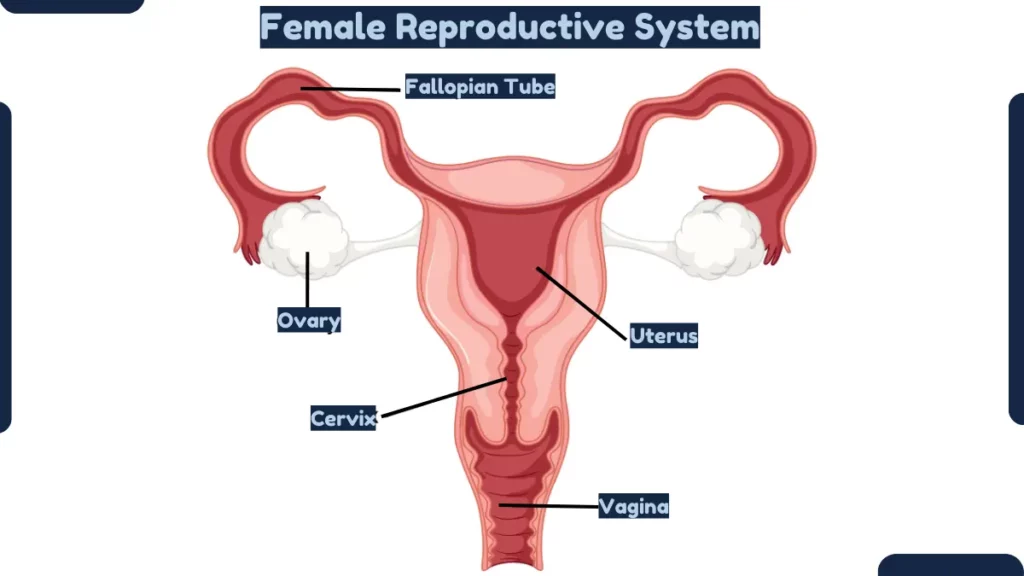
6. Vagina
The vagina is an elastic, muscular canal connecting the uterus to the exterior of the body. It receives sperm during intercourse and allows for childbirth and menstrual flow. The vagina can expand during childbirth and contract to hold a tampon.
7. Cervix
The cervix is the lower portion of the uterus that protrudes into the top of the vagina. It has an opening that dilates during childbirth to allow a baby to pass through. The cervix prevents internal items like tampons from getting lost inside the body.
8. Uterus
The uterus is a hollow, pear-shaped organ where fetal development occurs during pregnancy. It consists of the cervix and main body (corpus). The muscular corpus expands during pregnancy to hold the growing fetus.
9. Ovaries
The ovaries are almond-sized glands located on either side of the uterus. They produce eggs (ova) and hormones like estrogen and progesterone that control the menstrual cycle.
10. Fallopian Tubes
The fallopian tubes extend from the upper uterus to the area near the ovaries. Eggs travel from the ovaries to the uterus through these narrow tubes. Fertilization of eggs by sperm usually occurs here.
Functions of Female Reproductive System
- Produce eggs (ova) for fertilization.
- Provide a passageway for sperm to reach the eggs (fallopian tubes).
- Provide a site for fertilization (fallopian tubes).
- Provide a site for implantation of a fertilized egg (uterus).
- Provide an environment for the developing fetus (uterus).
- Facilitate childbirth (vagina, cervix, and vulva).
- Produce sex hormones (estrogen and progesterone) that regulate the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and other bodily functions.
- Protect against infection (vaginal flora and other protective mechanisms).
Also Read:



Leave a Reply