Nuclear Fission-Definition, Discovery, and Example
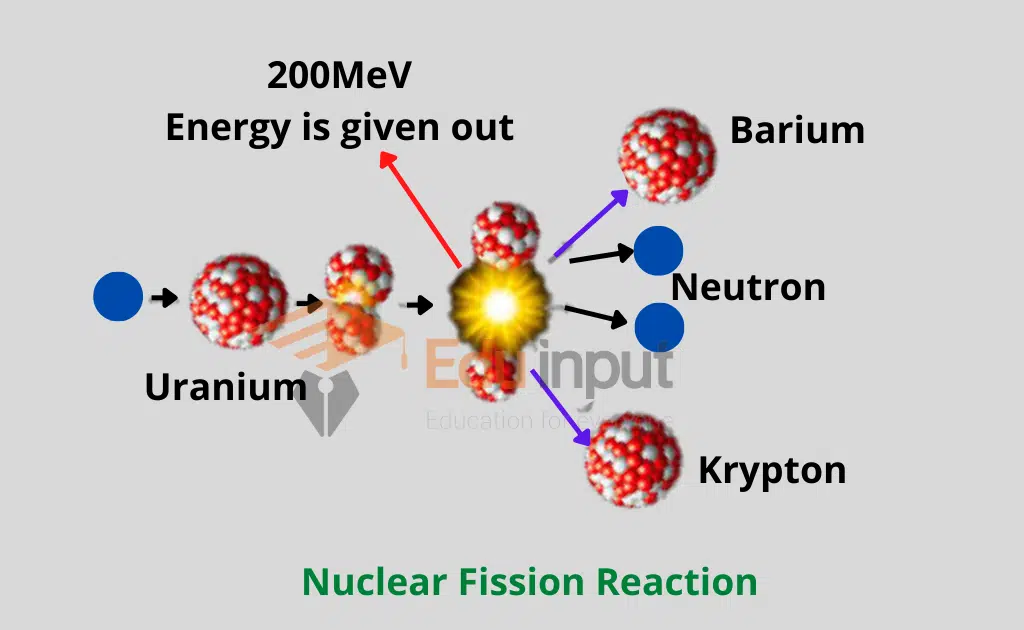
Nuclear fission is such a reaction in which a heavy nucleus like that of uranium splits up into two nuclei of roughly equal size along with the emission of energy during the reaction is called fission reaction. Nuclear fission is caused by the bombardment of heavy atomic nuclei.
Nuclear Fission
Nuclear fission is a reaction in which the nucleus of an atom splits into two or smaller nuclei. The fission process often produces gamma photons and releases a very large amount of energy even by the energetic standards of radioactive decay reactions.
In a nuclear fission reaction if we control the neutrons we can produce a fission chain reaction.
Discovery of Nuclear Fission
Otto Hahn and Fritz Strassmann of Germany while working on the nuclear reactions made a startling discovery. They observed that when slow-moving neutrons are bombarded on 23592U, then as a result of the nuclear reaction 14156Ba, 9236Kr, an average of three neutrons are obtained.
It may be remembered that the mass of both krypton and barium is less than that of the mass of uranium. This nuclear reaction was different from others to study other nuclear reactions, in two ways.
- First, as a result of the breakage of the uranium nucleus, two nuclei of almost equal size are obtained, whereas in the other nuclear reactions the difference between the masses of the reactants and the products was not large.
- Secondly, a very large amount of energy is given out in this reaction
“Such a reaction in which a heavy nucleus like that of uranium splits up into two nuclei of roughly equal size along with the emission of energy during the reaction is called fission reaction”.
Fission Reaction Example
The fission reaction of 23592U can be represented by the equation

Here Q is the energy given out in this reaction.
By comparing the total energy on the left side of the equation with the total energy on the right side, we find that in the fission of one uranium nucleus about 200 MeV energy is given out.
There is no difference between the sum of the mass and the charge numbers on both sides of the equation.
The binding energy per nucleon is greatest for the middle elements of the periodic table and this binding energy per nucleon is a little less for the light or very heavy elements.
The nucleons in the light or very heavy elements are not so rigidly bound. For example, the binding energy per nucleon for uranium is about 7.7 MeV and the products of the fission reaction of uranium, namely barium and krypton, have a binding energy of about 8.5 MeV per nucleon.
Thus when a uranium nucleus breaks up, as a result of a fission reaction, into barium and krypton, then energy at the rate of (8.5-7.6) = 0.9 MeV per nucleon is given out.
This means that energy 235 x 0.9=211.5 MeV is given out in the fission of one uranium nucleus.
The fission process of uranium does not always produce the same fragments (Ba, Kr). In fact, any of the two nuclei present in the upper horizontal part of binding energy could be produced.
Two possible fission reactions of uranium are given
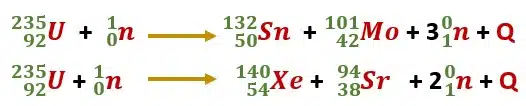
Hence in the uranium fission reaction, several products may be produced. All of these products (fragments) are radioactive.
Fission reaction is not confined to uranium alone; it is possible in many other heavy elements. However, it has been observed that fission takes place very easily with the slow neutrons in uranium-235 and plutonium-239, and mostly these two are used for fission purposes.
Related FAQs
What is nuclear fission?
Nuclear fission is the division of a heavy atomic nucleus into two fragments of equal mass. The release of a large amount of energy is a part of the process.
What causes nuclear fission?
When a neutron slams into a larger atom, it causes it to split into two smaller atoms, also known as fission products. A chain reaction can be initiated by the additional neutrons that are released. The amount of energy released when an atom splits is tremendous.
Why neutron is used in nuclear fission?
The positively charged nucleus isn’t able to repel the neutron since it doesn’t have a charge. It’s possible that a very weak neutron can bombard a nucleus. A very weak neutron can initiate a nuclear reaction by bombarding the nucleus. neutron is used for bombarding the nucleus in a nuclear reaction.






Leave a Reply