Which Homeostatic Process Is Characterized By The Diffusion Of Only Water Molecules?
The homeostatic process characterized by the diffusion of water molecules is osmosis.
Osmosis is the diffusion of water across a semipermeable membrane from a region of high water concentration to a region of low water concentration.
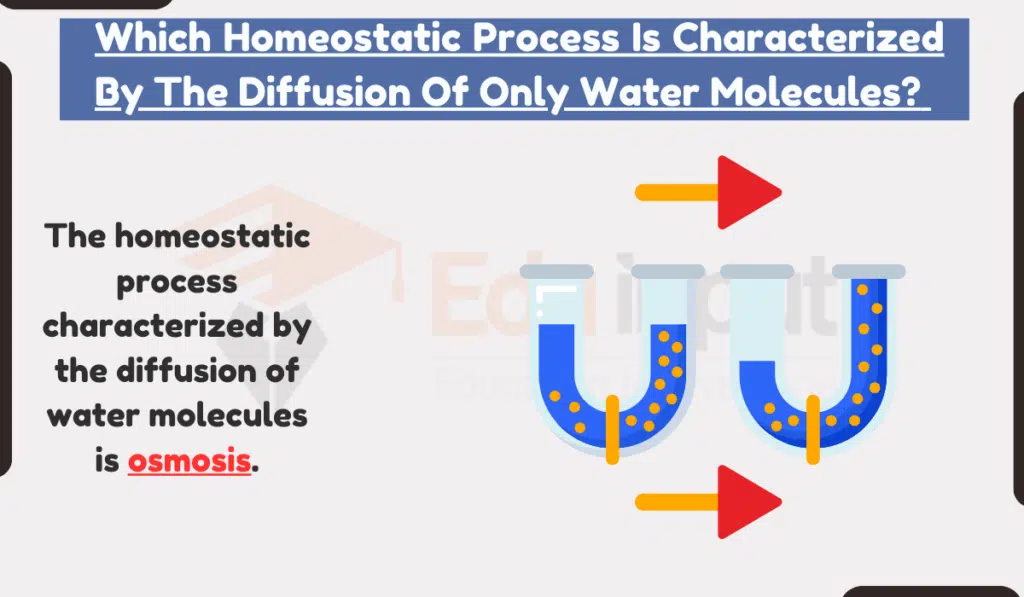
A semipermeable membrane is a membrane that allows some molecules to pass through but not others. Water molecules are small and uncharged, so they can easily pass through most semipermeable membranes.
Osmosis is a passive transport process, meaning that it does not require energy from the cell. Instead, it is driven by the difference in water concentration on either side of the membrane.
Water molecules will always move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration until equilibrium is reached.
Osmosis is responsible for maintaining the water balance of cells and tissues. Osmosis also plays a role in many other important physiological processes, such as nutrient absorption and waste removal.
Examples of Role of Osmosis in Homeostasis
Here are some examples of osmosis in the body:
- When you drink a glass of water, the water is absorbed into your bloodstream by osmosis.
- When you sweat, water molecules move from your blood to the surface of your skin by osmosis.
- When you eat a salty meal, water molecules move from your cells into the surrounding fluid by osmosis.
- When you have a kidney infection, bacteria can cause the walls of your kidney tubules to become more permeable. This can lead to osmosis of water from the blood into the tubules, resulting in increased urine production.
Learn more articles related to homeostasis:



Leave a Reply