What Are Microorganisms?-Definition, History, And Examples
Microorganisms are microscopic organisms that are classified into different groups such as bacteria, fungi, archaea, and protists. The study of these organisms is called microbiology. Advances in genome analysis have both simplified and complicated the classification process, but microorganisms are not placed in a specific kingdom.
They are placed with other organisms in different kingdoms based on their similarities with those organisms. Microorganisms make up the majority of life on Earth. But still, 99% of microorganisms are yet to be identified. Approximately 7,000 species of prokaryotes have been identified. source
Microorganisms are organisms that are microscopic and cannot be seen through the naked eye.
Definition of Microorganisms

Key Points
- Microorganisms are microscopic organisms found in every type of environment. They are adapted to survive in harsh conditions too.
- Microorganisms are classified such as bacteria, fungi, archaea, and protists.
- The study of Microorganisms is called microbiology.
- Microorganisms make up the majority of life on Earth and their diversity is vast. They make microbiome in multicellular organisms.
- Anton van Leeuwenhoek, Louis Pasteur, and Robert Koch are the key figures in the history of microbiology.
- Bacteria are prokaryotic microorganisms that function and reproduce as individual cells and have an extracellular circular chromosome named plasmid.
- Protozoa are single-celled organisms that are similar to animal cells and can move using cilia, flagella, or pseudopodia.
- Protists are a diverse group of unicellular organisms that can be difficult to classify due to their similarities with animals, plants and all other organisms.
- Fungi are microorganisms that play crucial role in the ecosystem by decomposing dead matter and forming symbiotic relationships with plants.
History Of Microorganisms And Microbiology
The idea of unseen forms of life has been present in human thought for a long time. Many evidences are present Even from the 6th century. These evidences suggest the possibility of microscopic life.
The invention of the microscope made it easy for scientists to understand these tiny creatures. Anton van Leeuwenhoek was the first ever scientist to provide detailed documentation of his observations of microorganisms.
He observed protozoa from the guts of animals and bacteria from teeth scrapings and recorded his findings in letters to the British Royal Society in the mid-1670s. It wasn’t known until the 18th century that people realized the importance of tiny organisms in the environment and human health.
In the 19th century, Louis Pasteur and Robert Koch made significant contributions to this field by disproving the theory of spontaneous generation. They established a link between microorganisms and diseases.
Later, microbiologists such as Martinus Beijerinck and Sergei Winogradsky expanded the understanding of the diversity and importance of microorganisms in various environments and their impact on human health and the environment.
Diversity Of Microorganisms
The diversity of microorganisms is wide. They are found in a vast range of environments. They can be found in polar regions, tropical areas, deserts, rocks, and even in the deep sea. Some microorganisms are adapted to live in extreme conditions such as high temperatures or cold temperatures, high pressure, highly alkaline environment, and even in high radiation environments.
All multicellular organisms have microbiomes in and on their bodies. This microbiome consists of microorganisms. This microbiome helps in different functions like the microbiome in the human gut helps in food digestion.
Organic compounds in old rocks have been discovered in old rocks. This discovery supports the theory that microbes were the first life on Earth. Thus studies have shown that microorganisms were present in these 3.45 billion-year-old rocks in Australia. It provides the evidence of earliest known life on Earth. source
Examples Of Microorganisms
Some examples of microorganisms include bacteria, archaea, fungi, algae, protozoa, and viruses. These different groups of microorganisms have distinct characteristics and play different roles in the nature.
Bacteria
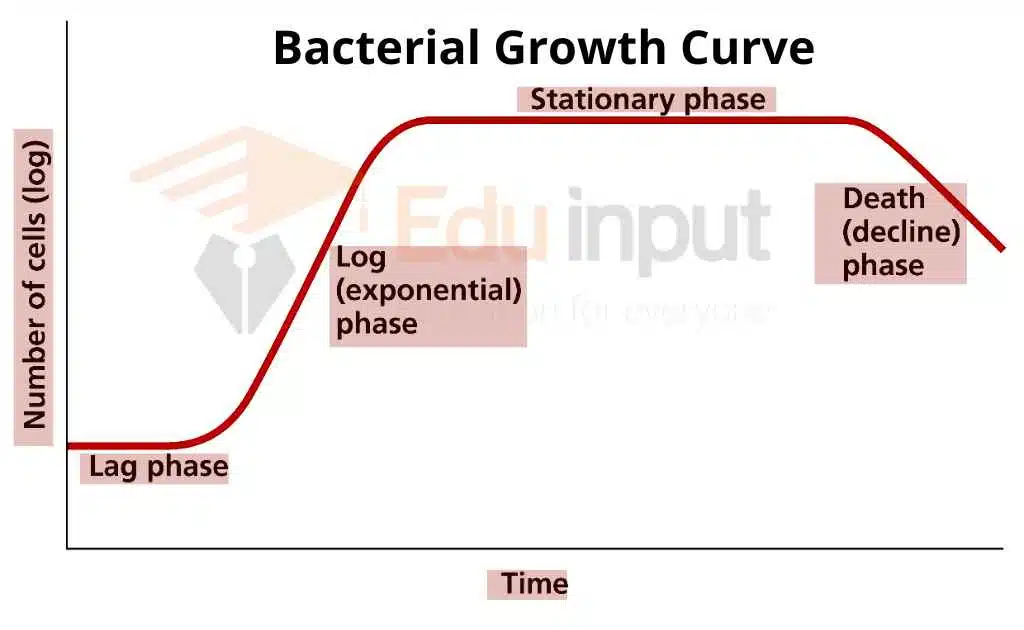
Bacteria are prokaryotic microorganisms that manage every biological process as individual cells. They may aggregate to form multicellular colonies and have circular chromosome chromosomes. They also contain small pieces of DNA called plasmids. They have a cell wall and reproduce through binary fission or budding. Meiotic sexual reproduction is absent in them. However, many bacterial species can transfer DNA through a process called natural transformation and conjugation. Some bacteria can form resilient spores as a survival mechanism and can reproduce very quickly.
Protozoa
Protozoa are single-celled organisms that are similar to animal cells. They can be of different shapes and sizes and can move using cilia or flagella. Some can also move by extending a part of their cell called a pseudopod. They can be found in natural environments, especially in water. Some protozoa, like amoebas, can change shape and move by extending pseudopodia. Other species like sporozoans, form dormant spores during certain life cycle stages.
Protists
Protists are microscopic unicellular organisms. These organisms have distinct characteristics that differentiates them from all other organisms.
Some protists, such as certain algae species, are multicellular. But other organisms such as slime molds, have unique life cycles that involve different forms of organization. They might be unicellular, colonial, or multicellular. The exact number of protist species is unknown yet, as only a small proportion of them have been identified.
However, it is believed that there are many more undiscovered species of protists due to the high diversity found in oceans, deep sea vents, river sediment, and an acidic river.
Fungi
Fungi are microorganisms that play a key role in the ecosystem by decomposing dead matter and organic material in soil and water. They are known for their ability to decompose cellulose, a major component of plant cells, and form symbiotic relationships with plants, such as mycorrhizal fungi, improving the plant’s water absorption and minerals.
Some species of fungi also produce enzymes that break down lignin, making it easier to digest.
Fungi play an important role in connecting different parts of the environment and maintaining the balance of nature through their diverse interactions with other organisms and the environment. source
Fungi are adapted to survive in extreme environments. They play an important role in maintaining the balance of harsh ecosystems. They can tolerate harsh conditions. This ability challenges current beliefs about the limits of life on Earth. source
Latest Research About Microorganism
- Scientists have conducted a critical review on whether microorganisms can cleave Si-C bonds in methyl siloxanes, a type of pollutant found in many environmental compartments. Although widely used, these compounds do not occur naturally. Despite their economic relevance, the review found no convincing evidence of Si-C cleavage by native environmental microorganisms. [source]
- Scientists have extensively studied the importance of maintaining sterility in medicine production. Injected medicines, called parenterals, must be sterile to prevent microorganisms from spreading throughout the body and causing illness. Cleanrooms equipped with special technologies are used to prevent contamination and ensure medicines are safe for patients. [source]
Frequently Asked Questions-FAQs
What are microorganisms?
Microorganisms are organisms that are microscopic and can not be seen with the naked eye.
What are the types of microorganisms?
Microorganisms are of the following types:
Bacteria
Archaea
Fungi
Protists
Viruses are not considered microorganisms as they are acellular (non-cellular) creatures.
What is a microbiome?
A microbiome is the collection of microorganisms that are present in a specific environment, for example all the microorganisms present in human body.
Who discovered microorganisms?
Antonie van Leeuwenhoek was the first ever scientist to provide detailed documentation of his observations of microorganisms.
How are microorganisms useful to humans?
Microbes are present in the human gut that help them in food digestion. They are also being used in biotechnology to aid human life. They are used to produce vaccines and antibiotics. They are commercially being used for curd preparation, fermentation, and brewery.
When did microbes first appear on Earth?
It is believed that the first form of life appeared on earth about 3.5-3.7 billion years ago. Organic matter was discovered in old rocks in Australia that gave the idea of the first form of life on earth.




Leave a Reply