Covalent Bond, definition, types, formation, Characteristics, Factors
Covalent bond definition
A covalent bond is formed when two atoms share one or more pairs of electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration.
Covalent bond Explanation
Covalent bonds become a fundamental force in the complex world of chemical bonding, reshaping the molecular environment. Unlike ionic bonds, where electrons are transferred, covalent bonds involve the shared ownership of electrons between atoms. This sharing of electrons fosters the creation of molecules with distinct properties, influencing the behavior of myriad substances in the natural world.
This sharing results in the formation of molecules, where atoms are held together by the mutual attraction of the shared electrons. Covalent bonds are prevalent in nonmetallic elements and are vital for constructing the vast diversity of compounds encountered in chemistry.
Types of Covalent Bonds
Single Covalent Bond
Involves the sharing of one pair of electrons between two atoms.
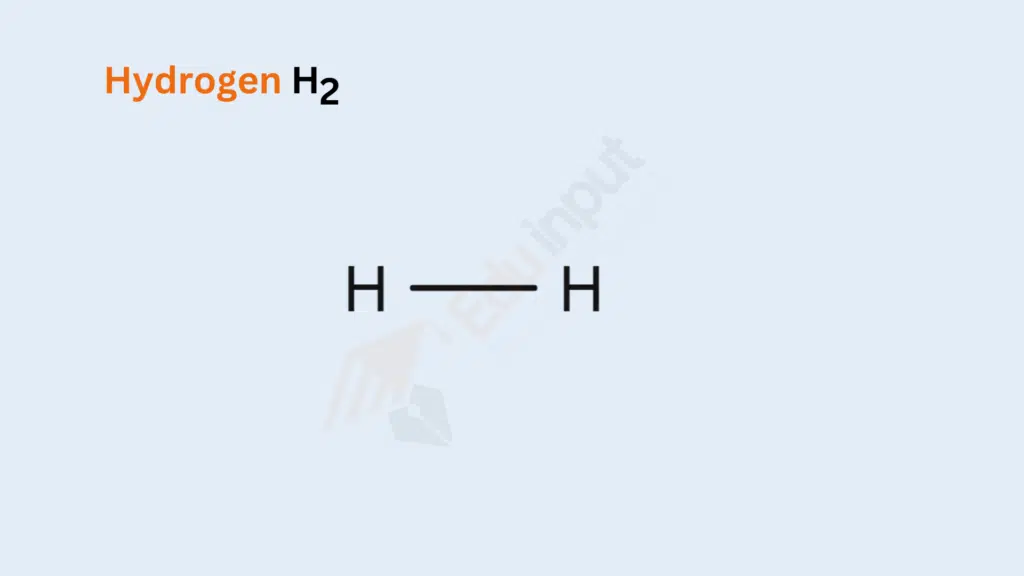
Bond Type: Single Covalent Bond
Formation: Two hydrogen atoms share a pair of electrons, forming a stable diatomic molecule.
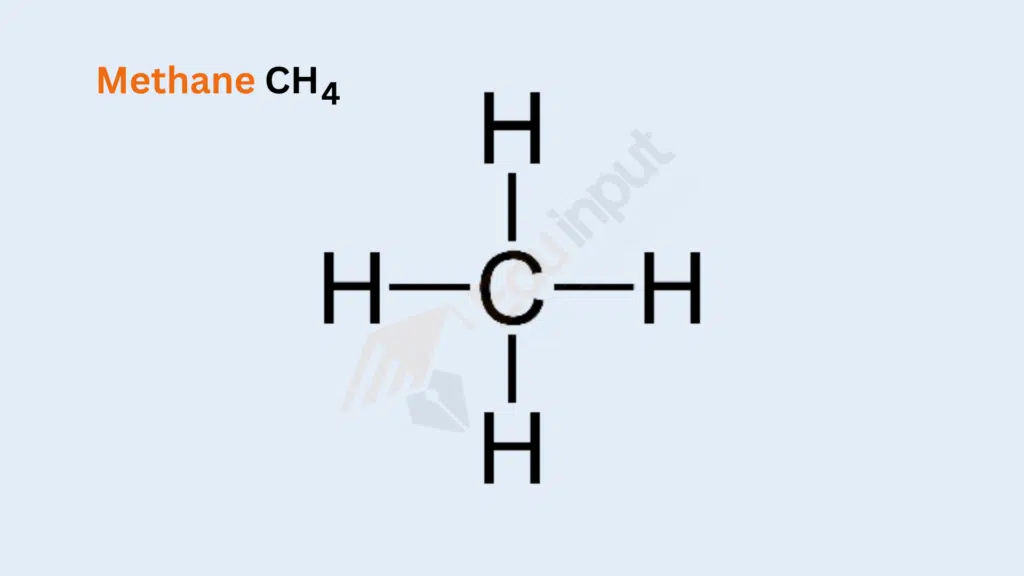
Methane (CH₄)
Bond Type: Single Covalent Bonds
Formation: Four hydrogen atoms share one pair of electrons with a central carbon atom.
Double Covalent Bond
Involves the sharing of two pairs of electrons between two atoms.
Oxygen Molecule (O₂)
Bond Type: Double Covalent Bond
Formation: Two oxygen atoms share two pairs of electrons, resulting in the formation of a diatomic oxygen molecule.

Triple Covalent Bond
Involves the sharing of three pairs of electrons between two atoms.
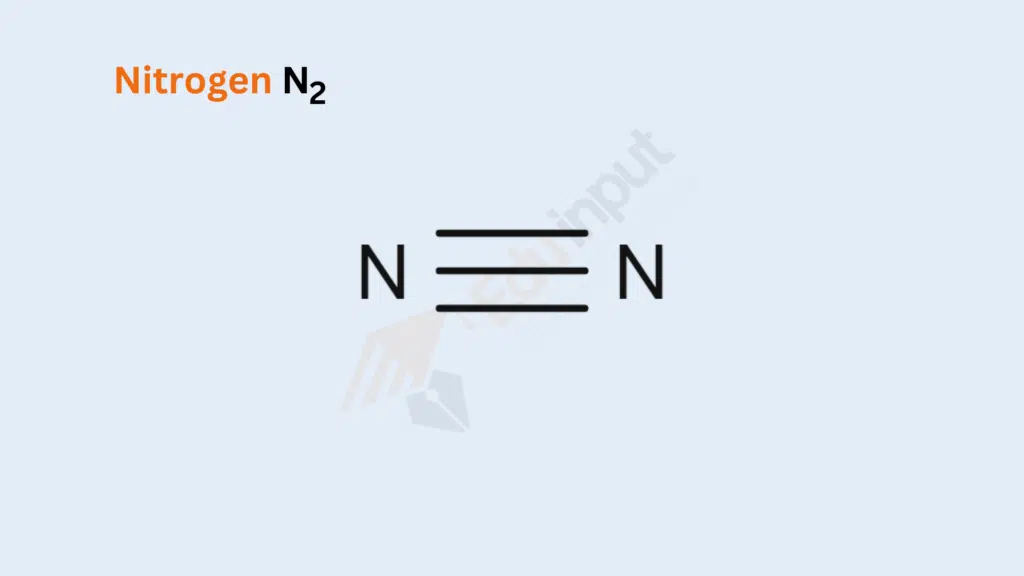
Nitrogen Gas (N₂)
Bond Type: Triple Covalent Bond
Formation: Two nitrogen atoms share three pairs of electrons to achieve a stable molecular structure. Each nitrogen atom contributes three electrons, resulting in the formation of a triple covalent bond between them. The molecular formula for nitrogen gas is N₂.
Formation of Covalent Bonds
Electron Sharing
Atoms share electrons to achieve a full outer electron shell and attain stability.
Octet Rule
Atoms tend to share electrons to achieve an electron configuration similar to that of noble gases, typically eight electrons in the outer shell.
Characteristics of Covalent Compounds:
Low Melting and Boiling Points
Covalent compounds often have lower melting and boiling points compared to ionic compounds.
Poor Conductors of Electricity
Covalent compounds in their pure state generally do not conduct electricity because the electrons are localized between the bonded atoms.
Solubility in Nonpolar Solvents
Many covalent compounds dissolve well in nonpolar solvents due to similar intermolecular forces.
Factors Influencing Covalent Bonding
Electronegativity Difference
Small or negligible electronegativity differences between atoms favor covalent bonding because such atoms have similar tendencies to attract electrons. This leads to the formation of molecules where electrons are shared, resulting in a more stable configuration for both atoms.
Atomic Size
Atoms of similar size are more likely to form covalent bonds because their similar orbital sizes, energy levels, and electron distributions allow for effective and efficient overlap of orbitals, leading to the stable sharing of electrons.
Orbital Overlap
The efficient overlap of atomic orbitals is essential for the formation of strong covalent bonds. It maximizes the shared electron density between atoms, minimizes potential energy, and contributes to the overall stability and strength of the covalent bond.
What is a covalent bond?
A covalent bond is a type of chemical bond formed when two atoms share electrons. It occurs between nonmetal atoms and is characterized by the mutual sharing of electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration.
How is a covalent bond different from an ionic bond?
In a covalent bond, electrons are shared between atoms, leading to the formation of molecules. In contrast, an ionic bond involves the transfer of electrons from one atom to another, resulting in the formation of ions.
What are the types of covalent bonds?
Covalent bonds can be classified into single, double, and triple bonds. A single covalent bond involves the sharing of one pair of electrons, a double bond involves the sharing of two pairs, and a triple bond involves the sharing of three pairs.
How does electronegativity influence covalent bonding?
Electronegativity differences between atoms influence the nature of covalent bonds. Small or negligible differences lead to nonpolar covalent bonds, while moderate differences result in polar covalent bonds.
What are the characteristics of covalent compounds?
Covalent compounds often have lower melting and boiling points compared to ionic compounds. They are generally poor conductors of electricity in their pure state and tend to have varying solubility’s in different solvents based on their polarity.






Leave a Reply