10 Differences Between Solvent Extraction and Distillation
The main difference between solvent extraction and distillation is the difference in their fundamental processes and objectives. Solvent extraction depends on solubility for selective compound separation, while distillation uses variations in boiling points for component isolation.
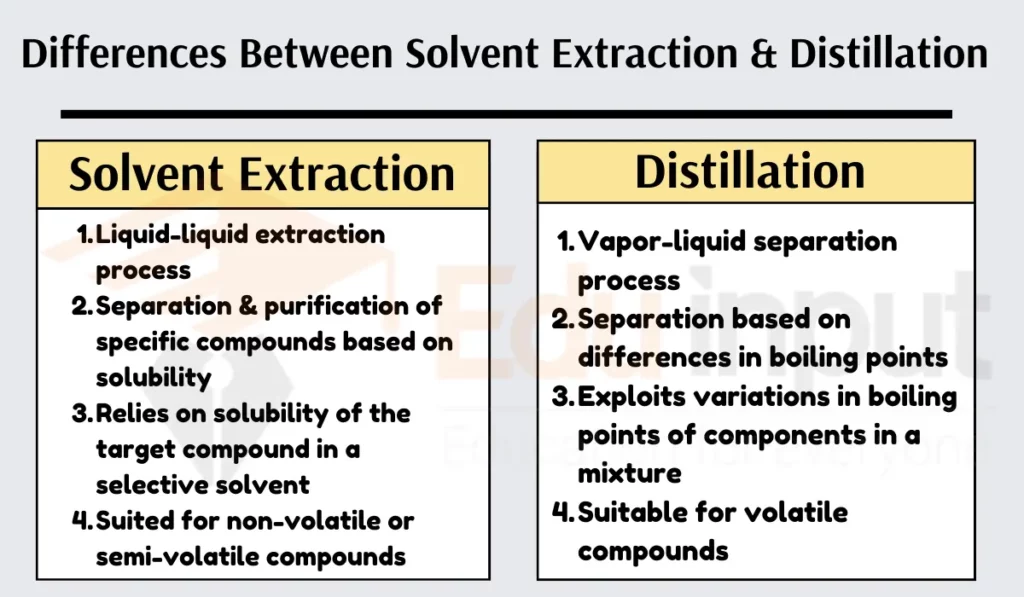
Differences Between Solvent Extraction and Distillation
Here is a comparative analysis of Differences Between Solvent Extraction and Distillation:
Process Type
Solvent extraction involves a liquid-liquid extraction, while distillation uses a vapor-liquid separation.
Objective
Solvent extraction aims to separate and purify specific compounds from a mixture. At the same time, distillation focuses on separating components based on their boiling points.
Principle
Solvent extraction relies on the solubility of the target compound in a selective solvent. At the same time, distillation exploits differences in the boiling points of components in a mixture.
Nature of Components
Solvent extraction is typically used for nonvolatile or semivolatile compounds, while distillation is suitable for volatile compounds.
Temperature Requirement
Solvent extraction generally operates at room or slightly elevated temperatures. At the same time, distillation requires heating to reach and maintain specific boiling points.
Equipment
Solvent extraction utilizes extraction vessels and separation funnels, while distillation involves distillation columns, condensers, and receivers.
Energy Consumption
Solvent extraction typically has lower energy consumption than distillation, while distillation incurs higher energy consumption due to heating.
Applications
Solvent extraction is widely used to extract natural products, flavours, and fragrances. At the same time, distillation is commonly employed to purify liquids, such as water or alcohol.
End Product
Solvent extraction yields a concentrated solution of the target compound in the solvent. At the same time, distillation produces separate fractions based on boiling points, with the potential for further Purification.
Examples of Usage
Solvent extraction finds applications in the extraction of essential oils from plants and the Separation of organic compounds. At the same time, distillation is commonly used to Purify alcohol and separate components in crude oil refining.
Solvent Extraction vs Distillation
| It relies on the solubility of the target compound in a selective solvent | Solvent Extraction | Distillation |
|---|---|---|
| Process Type | Liquid-liquid extraction | Vapor-liquid separation |
| Objective | Separation and purification of specific compounds from a mixture | Separation of components based on their boiling points |
| Principle | Relies on the solubility of the target compound in a selective solvent | Exploits differences in boiling points of components in a mixture |
| Nature of Components | Typically used for non-volatile or semi-volatile compounds | Suitable for volatile compounds |
| Temperature Requirement | Generally operates at room temperature or slightly elevated temperatures | Requires heating to reach and maintain specific boiling points |
| Equipment | Utilizes extraction vessels and separation funnels | Involves distillation columns, condensers, and receivers |
| Energy Consumption | Typically lower energy consumption compared to distillation | Higher energy consumption due to the need for heating |
| Applications | Widely used in the extraction of natural products, flavors, and fragrances | Commonly employed in the purification of liquids, such as water or alcohol |
| End Product | Yields a concentrated solution of the target compound in the solvent | Produces separate fractions based on boiling points, with potential for further purification |
| Examples of Usage | Extraction of essential oils from plants, separation of organic compounds | Purification of alcohol, separation of components in crude oil refining |
Also Read:
Factors That Affect Solvent Extraction
Which Properties of Solvents are Useful for Solvent Extraction?



Leave a Reply