20 Examples of Membranes
Cell membranes, nuclear membranes, mitochondrial membranes, and endoplasmic reticulum membranes are some examples of membranes in biological systems.
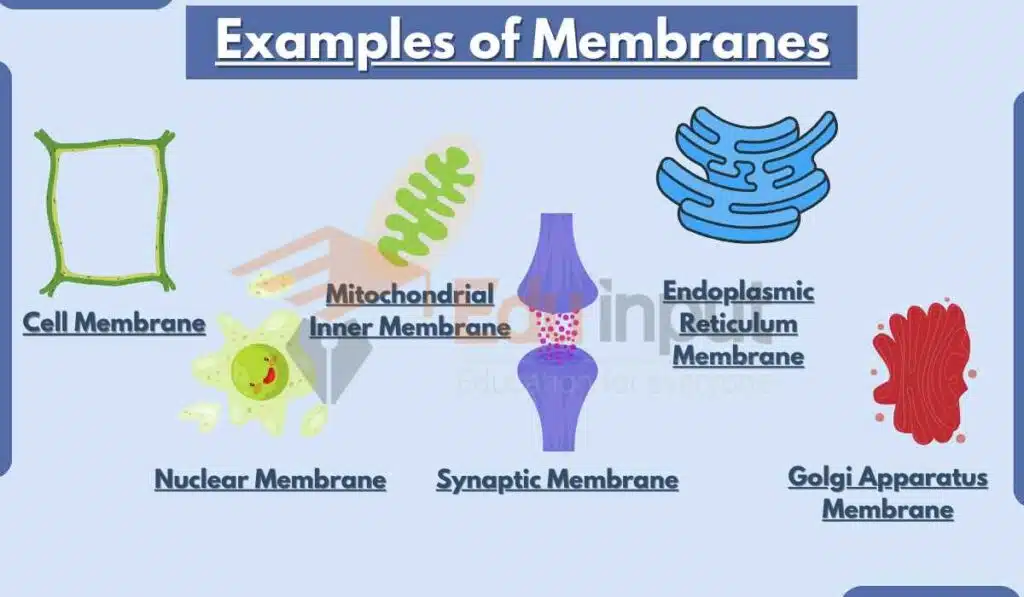
Examples of Membranes
Membranes are important components in various biological, industrial, and technological processes.
They act as barriers or separators and allow selective passage of substances while blocking others.
Here are 20 examples of membranes:
1: Cell Membrane
The most common example of membrane is a cell membrane. It is part of all living cells. It regulates the passage of ions and molecules. It also maintains cellular integrity.
2: Lipid Bilayer
The lipid bilayer is composed of phospholipids arranged in a double layer, providing the membrane’s fluidity.
3: Nuclear Membrane
The nuclear membrane, or nuclear envelope is an example of the membrane that encloses the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. It controls the flow of materials in and out of the nucleus.
4: Mitochondrial Inner Membrane
This inner membrane of mitochondria forms folds called cristae. It is where most of the ATP production occurs in mitochondria.
5: Endoplasmic Reticulum Membrane
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) has a complex membrane system involved in protein synthesis and lipid metabolism.
6: Golgi Apparatus Membrane
The Golgi apparatus sorts modifies, and packages proteins and lipids into vesicles for transport, utilizing its membrane network.
7: Synaptic Membrane
Another example of a membrane is the membrane found at the junction between nerve cells. This synaptic membrane plays an important role in neurotransmitter release and signal transmission.
8: Capillary Membrane
Capillary walls consist of thin membranes, allowing the exchange of nutrients, gases, and waste products between blood and tissues.
9: Artificial Membrane
Artificial membranes, such as dialysis membranes, mimic biological membranes and are used in medical applications for filtration and separation.
10: Permeable Membrane
Permeable membranes are engineered to allow specific substances to pass through while excluding others, commonly used in water filtration.
11: Semipermeable Membrane
Semipermeable membranes partially allow the passage of certain molecules while blocking others, used in osmosis and dialysis.
12: Selective Barrier
Biological membranes act as selective barriers, controlling the movement of ions, nutrients, and signaling molecules.
13: Mucous Membrane
Mucous membranes line various body cavities, including the respiratory and digestive tracts, providing protection and facilitating absorption.
14: Electrolyte Membrane
Electrolyte membranes are used in fuel cells to conduct ions and enable chemical reactions that produce electricity.
15: Photoreceptor Membrane
In the retina, photoreceptor cells contain specialized membranes that capture light and initiate vision.
16: Chloroplast Membrane
Chloroplasts, found in plant cells, have membranes that house the photosynthetic machinery, converting light energy into chemical energy.
17: Desalination Membrane
Desalination membranes are employed in reverse osmosis systems to remove salt and impurities from seawater, providing freshwater.
18: Synthetic Membrane
Synthetic membranes are engineered for various purposes, including artificial organs, drug delivery, and separating chemicals in industry.
19: Plasma Membrane of Bacteria
Bacterial cells have plasma membranes that maintain cell integrity and serve as targets for antibiotics.
20: Oxygen Permeable Membrane
These specialized membranes allow the controlled passage of oxygen and are used in medical devices like oxygen concentrators.





Leave a Reply