Lymphatic System-Components And Functions
The lymphatic system is a network of lymph vessels and lymph nodes throughout the body. The lymphatic system helps remove waste from the body and regulate immune function.
The lymphatic system consists of collecting lymphatics and transporting lymph. Collecting lymphatics collect fluid from tissues and organs and transport it to lymph nodes, which are filtered and cleaned before being returned to the bloodstream. Transporting lymphatics carries lymphocytes (white blood cells) from lymph nodes to other parts of the body.
Lymphatic system transports and returns material from tissues of the body to blood. The lymphatic system plays a vital role in maintaining health and well-being. In addition, it also has important functions in regulating immunity and removing toxins from the body.
What is Lymph?
The fluid that flows in the lymphatic system is called lymph. Lymph is an intermediate fluid between interstitial fluid and blood.
Factors Maintaining The Flow Of Lymph
The flow of lymph within the lymph vessels and thoracic duct is maintained by the following factors:
a) Activity of the skeletal muscles
b) Movement of viscera (body organ) like abdominal movements
c) Breathing movements
d) The lymph vessels have a valve. These valves prevent the backflow. So the lymph moves in the forward direction.
Component Of Lymphatic System
The lymphatic system consists of lymph capillaries, lymph vessels, lymphoid masses, and lymph node;
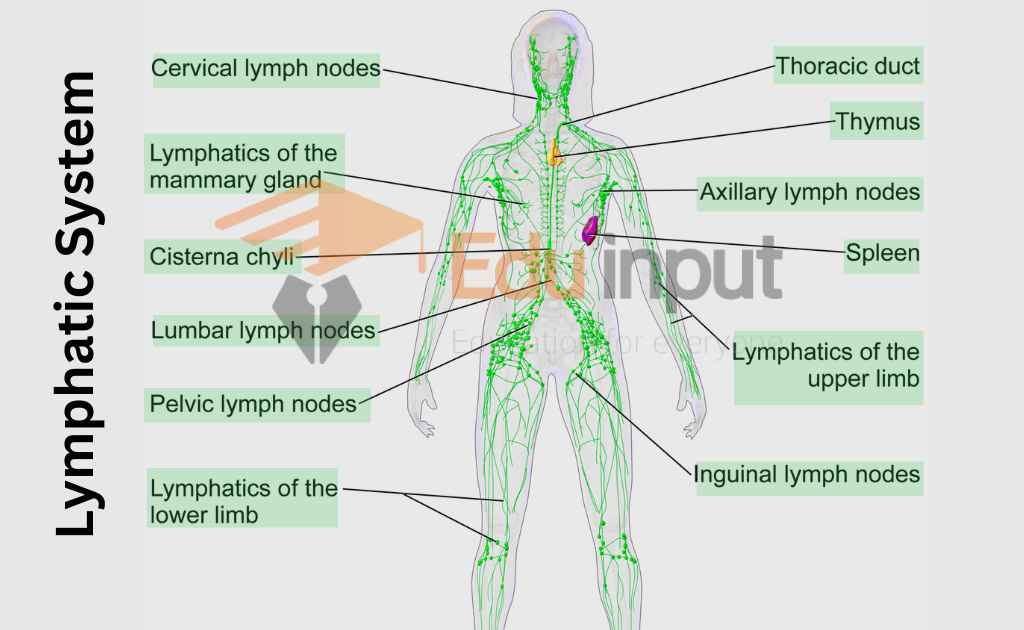
Lymph Capillaries
The lymph capillaries end blindly in the body tissues. There is an accumulation of interstitial d or extracellular fluid between the cells of the body tissues. This fluid produces pressure. This pressure forces the fluid into the lymph capillaries. When this fluid enters the lymph capillaries it is called lymph.
The intracellular spaces in the wall of the lymph capillaries are larger than the intracellular spaces in the walls of blood capillaries. Therefore, large molecules can also enter from the interstitial fluid into lymph capillaries. The branches of lymph capillaries in the villi (small intestine) are called lacteals.
Lymph Vessels
The lymph capillaries join to form larger and larger lymph vessels.
Thoracic Ducts
The lymph vessels ultimately form the thoracic lymph duct. The flow of lymph is always toward the thoracic duct. These thoracic lymph ducts open into a subclavian vein (shoulder vein).
Lymph Nodes
Lymph nodes are masses of connective tissues present at certain points along the pathways of lymph vessels. Lymphocytes (WBC) are present in these lymph nodes. Lymph nodes are present in the neck region, and groin area of humans.
Lymph nodes have two types of vessels:
a) Afferent lymph vessels: The lymph vessels that supply lymph to lymph nodes are called afferent lymph vessels. Several afferent vessels enter lymph nodes.
b) Efferent lymph vessel: There is only one efferent lymph vessel. It brings back lymph from lymph node into the lymph vessels
Lymphoid Masses
Several lymphoid masses are present in the mucosa and submucosa of the wall of the digestive tract, the spleen, tonsils, and adenoids (in the wall of the nasopharynx) have large lymphoid masses.
The lymphoid masses produce lymphocytes.
Functions Of The Lymphatic System
The lymphatic system performs several functions.
1. Reabsorption of tissue fluid: About three liters or more fluid leaves the blood capillaries in an average person. The blood capillaries reabsorb only a small amount of this fluid. The lymphatic system returns this excess fluid and dissolved proteins into the blood.
2. Absorption of fats in the digestive system: Certain interstitial cells absorb the product of fat digestion and release fat globules. The lacteals of the villi absorb these large fat globules. The fat globules become 1% of the lymph after a fatty meal.
3. Role in defense: The lymphatic system defends the body against foreign invaders. The lymph nodes have lymphocytes and macrophages. These lymphocytes and macrophages destroy the bacteria and viruses The dead lymphocytes and macrophages are accumulated in lymph nodes in certain diseases like mumps. So these lymph nodes are swelled painfully.
4. Filtration of blood: The spleen filters the blood. Similarly, lymph nodes filter the lymph and remove the foreign particles and aged red blood cells from the lymph. The macrophages and lymphocytes destroy these foreign particles.
Related FAQs
What is the lymphatic system?
Lymphatic system transports and returns material from tissues of the body to blood.
What are the components of the lymphatic system?
The lymphatic system consists of lymph capillaries, lymph vessels, lymphoid masses, and lymph nodes.
What are the functions of the lymphatic system?
The lymphatic system performs the following functions;
Reabsorption of tissue fluid
Absorption of fats in the digestive system
Role in defense
Filtration of blood
What are the organs of lymphatic system?
The lymphatic system involves the following organs;
Bone marrow
Spleen
Thymus
Lymph nodes
Lymphatic vessels
What is lymph?
The fluid that flows in the lymphatic system is called lymph. Lymph is an intermediate fluid between interstitial fluid and blood.




Leave a Reply