Role Of The Liver In Digestion
The liver is a major organ responsible for many functions including detoxification, protein synthesis, hormone production, blood clotting, and bile secretion. In addition, it is also responsible for storing glycogen (a type of carbohydrate) and fat.
The liver is located at the bottom of the right side of the abdomen behind the stomach. The liver is about the size of a fist and weighs between 1-2 pounds.
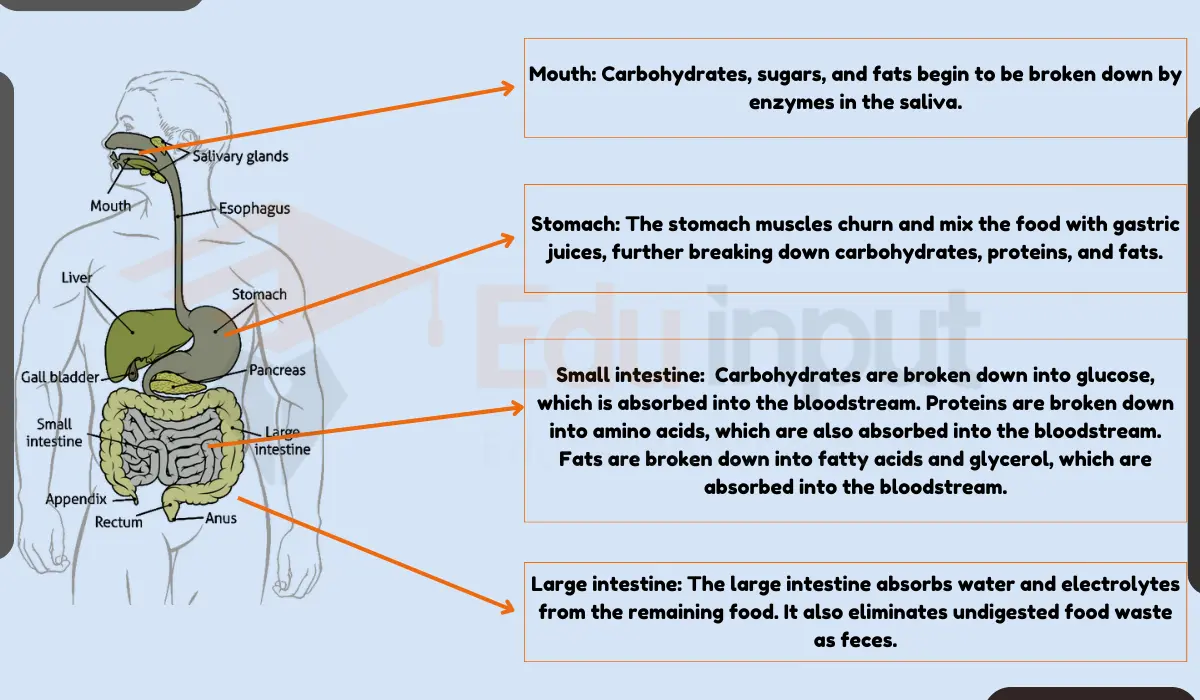
Also Read How Food is Absorbed In Our Body
The liver is the largest organ in the mammalian body. It lies just under the diaphragm. The liver has millions of specialized cells called Hepatocytes. These cells take nutrients absorbed from the intestines. They release them into the blood. Hepatocytes also synthesize the blood proteins Prothrombin and albumin.
Role Of Liver In Digestion
The liver has the following major metabolic functions:
1. It removes amino acids from organic compounds.
2. It forms urea from proteins. It converts excess amino acids into urea. It decreases body levels of ammonia.
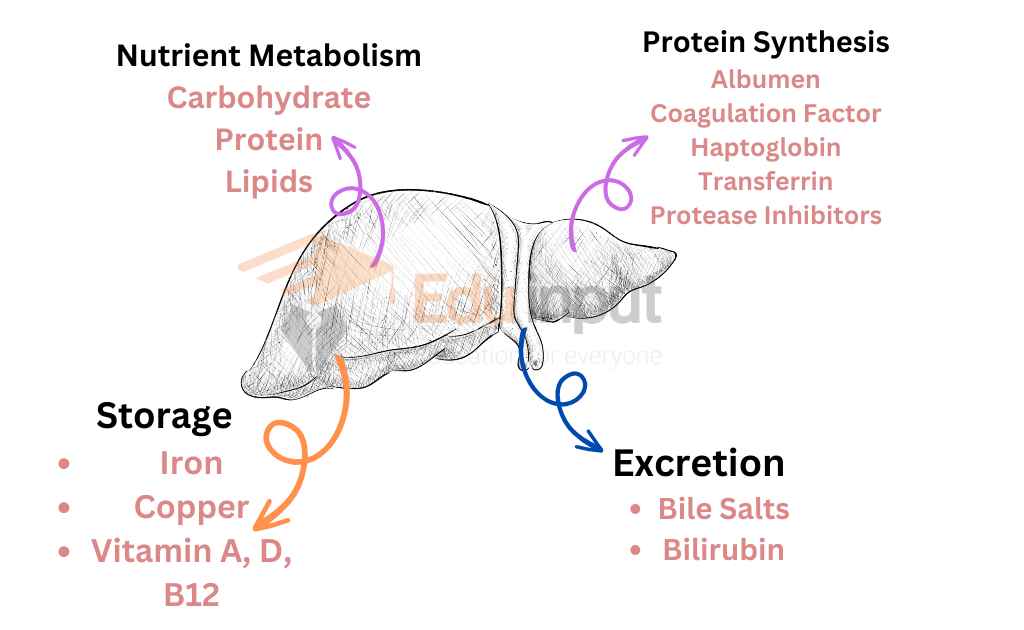
3. It synthesizes most of the plasma proteins. It forms the fetal erythrocytes. It destroys the worn-out (useless) erythrocytes. It synthesizes the blood-clotting agent prothrombin and fibrinogen from amino acids.
4. It synthesizes non-essential amino acids.
5. It converts galactose and fructose to glucose.
6. It causes the oxidation of fatty acids.
7. It forms lipoproteins, cholesterol, and phospholipids. These are essential cell membrane components.
8. It converts carbohydrates and proteins into fat.
9. It modifies waste products, toxic drugs, and poisons (detoxification).
10. It synthesizes vitamin A from carotene. It along with the kidney activates vitamin D.
11. It maintains a stable body temperature. Its many metabolic activities produce heat. Thus it raises the temperature of the blood passing through it.
12. It synthesizes bile salts. These salts are used in the small intestine to emulsify and absorb simple fats, cholesterol, phospholipids, and lipoproteins.
13. It is the main storage center. The liver stores glucose in the form of glycogen. It converts glycogen back into glucose with the help of insulin and enzymes. The liver also stores fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K). It also stores minerals like iron. The liver can also store fats and amino acids. It converts them into usable glucose.
Frequently Asked Questions-FAQs
What is the role of the liver in digestion?
The liver synthesizes bile salts, acts as a storage organ, and saves Vitamins and mineral ions. It is also involved in other vital functions.
How liver act as storage organ?
The liver is the main storage center. It stores glucose in the form of glycogen. It also converts glycogen back into glucose with the help of insulin and enzymes. The liver also stores fat–soluble vitamins, fats, amino acids, and minerals like iron.
What type of proteins are synthesized by the Liver?
The liver synthesizes most of the plasma membranes. It synthesizes clotting factor prothrombin and fibrinogen.




Leave a Reply