Xenon-Discovery, Properties, And Applications
October 19, 2023
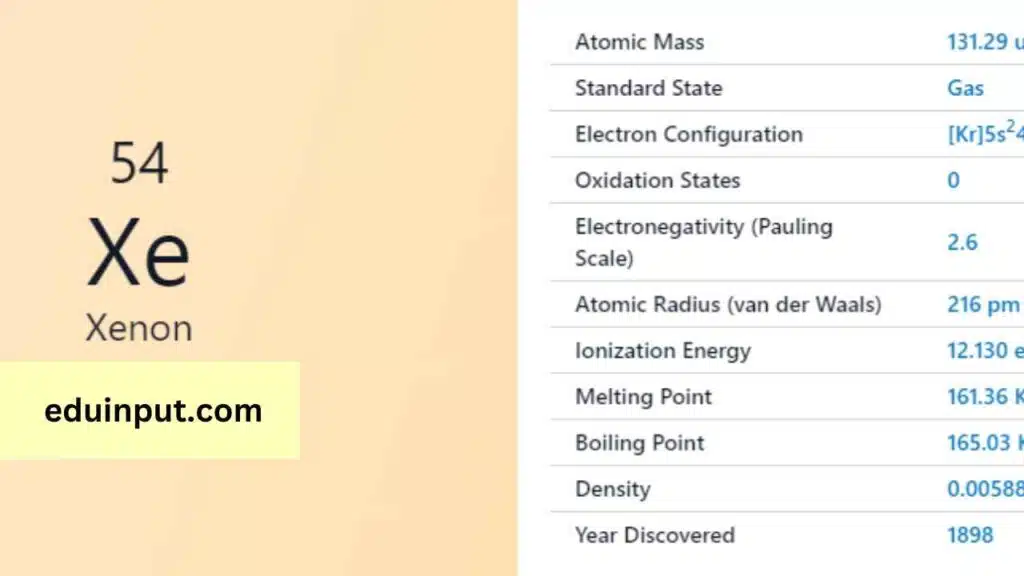
Xenon is a chemical element with the symbol Xe and atomic number 54. It is a colorless, dense, odorless noble gas found in trace amounts in the atmosphere.
| Property | Value |
| Name | Xenon |
| Symbol | Xe |
| Atomic number | 54 |
| Relative atomic mass (Ar) | Group in the periodic table |
| Standard state | Gas at 298 K |
| Appearance | Colourless |
| Classification | Non-metallic |
| Period in the periodic table | 18 |
| Group name | Noble gas |
| Block in the periodic table | 5 |
| Block in periodic table | p |
| Shell structure | 2.8.18.18.8 |
| CAS Registry | 7440-63-3 |
Table of Contents
Discovery
Xenon was discovered in England in 1898 by the chemist Sir William Ramsay and his assistant Morris Travers.
Physical Properties
- Atomic mass: 131.293 u
- Melting point: -111.9°C
- Boiling point: -107.1°C
- Density: 5.894 g/L
- It is a colorless, dense, odorless noble gas.
Chemical Properties
- Xenon is a noble gas and is very unreactive.
- It forms very few chemical compounds.
- It can form compounds with fluorine and oxygen.
Facts
- Xenon is used in various lighting applications such as flash lamps, strobe lights, and lamps for airport runways.
- It is also used in nuclear energy production and in medical imaging.
- Xenon is used as an anesthetic in medicine due to its non-toxicity and non-reactivity.
Applications
- Lighting: Xenon is used in various lighting applications such as flash lamps, strobe lights, and lamps for airport runways.
- Medical imaging: Xenon is used in medical imaging due to its ability to be detected by specialized equipment.
- Nuclear energy: Xenon is used in nuclear energy production due to its ability to absorb neutrons.
- Anesthesia: Xenon is used as an anesthetic in medicine due to its non-toxicity and non-reactivity.
Overall, xenon is a unique noble gas with a variety of applications in industries such as lighting, medical, and nuclear.
File Under:




Leave a Reply