Nuclear Transmutation | Decay Reactions, Alpha Decay, Beta Decay, and Gama Decay
Nuclear transmutation is the conversion of one radioactive element into another radioactive element. In nuclear transmutation, different types of radiation are produced. Uses of radiation in different fields of life have expanded tremendously.
What is Nuclear Transmutation?
Radioactivity is purely a nuclear phenomenon. Nuclear transmutation is a type of nuclear reaction. This is not affected by any physical or chemical reaction. Whenever any particle or radiation is emitted out of any radioactive element, it is always accompanied by some changes in the nucleus of the element.
Therefore, this element changes into a new element. This phenomenon is called radioactive decay.
The element formed due to this change is called the daughter element. The original element is called the parent element.
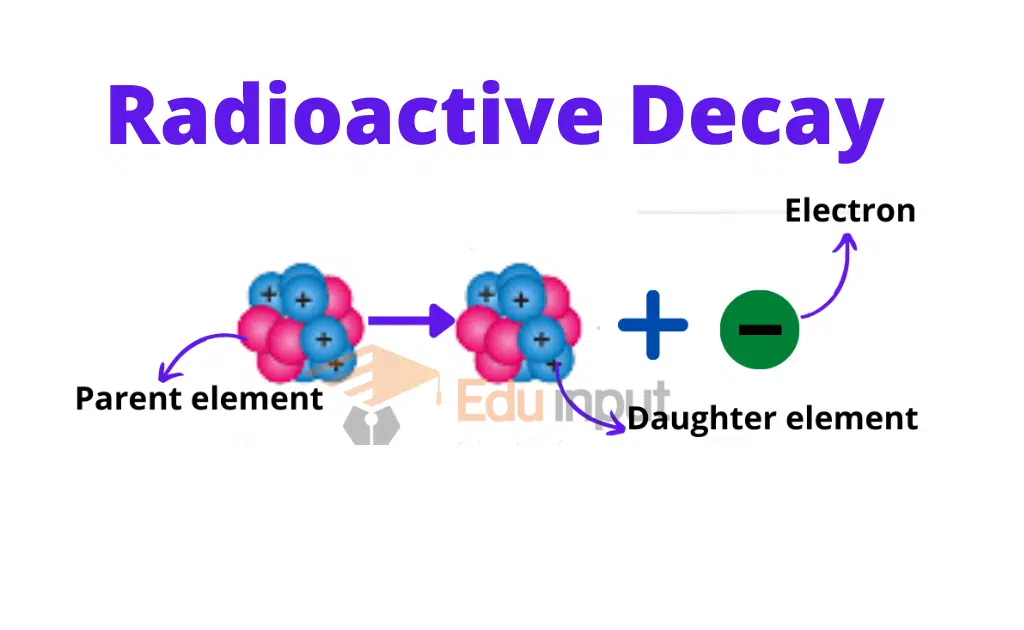
During the nuclear changes the law of conservation of momentum, mass, energy, and charge remains applicable.
Three types of radiation α-particle, β-particle, and γ-rays are emitted by naturally occurring radioactive elements. The range of these particles depends on the interaction of radiation with matter.
Alpha Decay
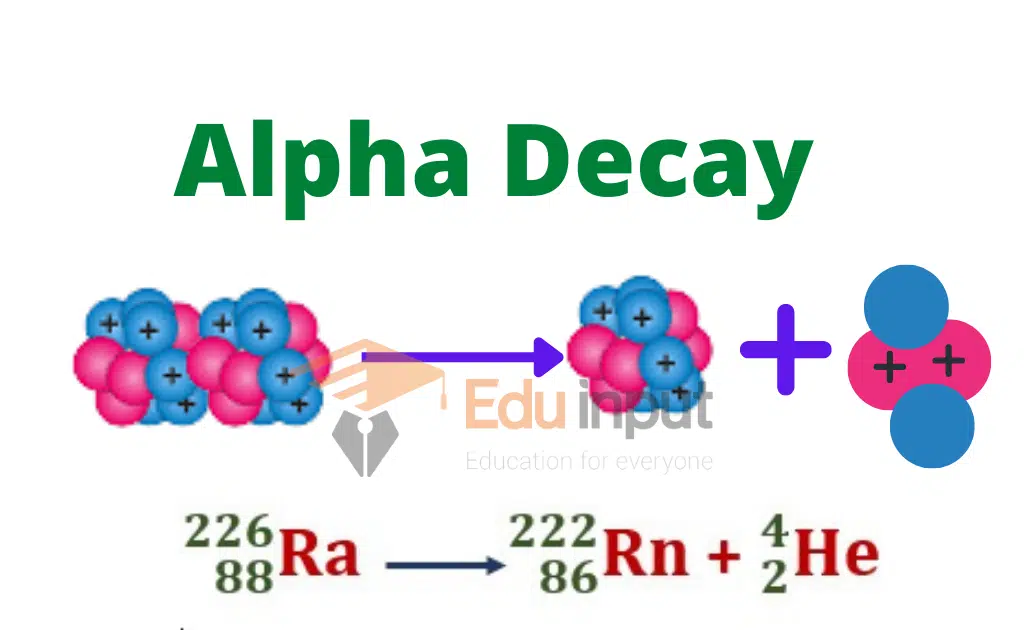
Alpha decay occurs when a particle is emitted out of any nucleus then due to the law of conservation of matter the mass number of the nucleus decreases by 4, and due to the law of conservation of charge, the charge of the nucleus decreases by a magnitude of 2e.
The charge number of the nucleus decreases by 2. It is due to the fact that the mass number and charge number of the emitted particle a are 4 and 2 respectively.
Alpha Decay Equation
The emission of the α-particle is represented as
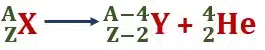
Here X represents the parent and Y the daughter element.
Example: The emission of an α-particle from radium Ra, results in the formation of radon gas Rn. This change is represented by the following equation
It may be remembered that the sum of the mass numbers and the charge numbers on both sides of the equation are equal.
Beta Decay
Beta decay occurs when a β-particle is emitted out of the nucleus. Then its mass number does not undergo any change but its charge number increases by one.
Beta Decay Equation
The emission of the β-particle from any element X is represented as
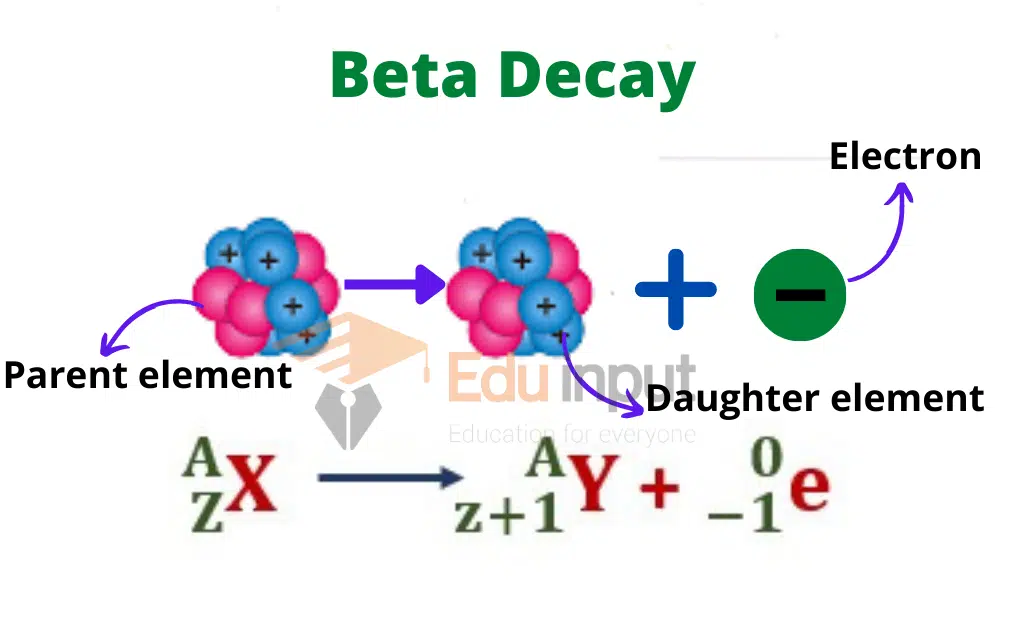
A negative β-particle is an electron and its emission from the nucleus becomes an unsolvable mystery, as then no electron is present in the nucleus.
However, the emission of electrons from the nucleus can be thought of as a neutron emitting an electron and becoming a proton, although the modern explanation is not that simple.
This means that the β-particle is formed at the time of emission.
That is why at the time of emission of a β-particle the charge number of the nucleus increases by one but no change in its mass number takes place as the mass of an electron is exceedingly small as compared to the mass of a proton or a neutron.
The transformation of an electron at the moment of its emission is given
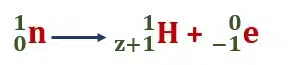
Example:
Thorium 23490Th transforms into protactinium 23491Pa after the emission of β-particle
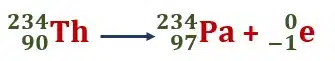
Gamma Decay
When γ-radiation issues out of the nucleus then neither the charge number Z nor the mass number A of the nucleus undergoes any change.
It is due to the fact that a γ-radiation is simply a photon that has neither any charge nor any mass. Its emission from the nucleus has some resemblance with the emission of a photon of light from an atom.
When any electron of an atom absorbs energy it jumps from the ground state to a higher energy state and the atom becomes excited.
When the electron of this excited atom returns to its ground state then it emits the absorbed energy in the form of a photon.
In much the same way the nucleus is sometimes excited to a higher state following the emission of α or β-particle.
Gamma Decay Equation
This excited state of the nucleus is an unstable state, in coming back to its ground state from the excited state, γ-radiation is emitted. The emission of γ-radiation from a nucleus is generally represented as
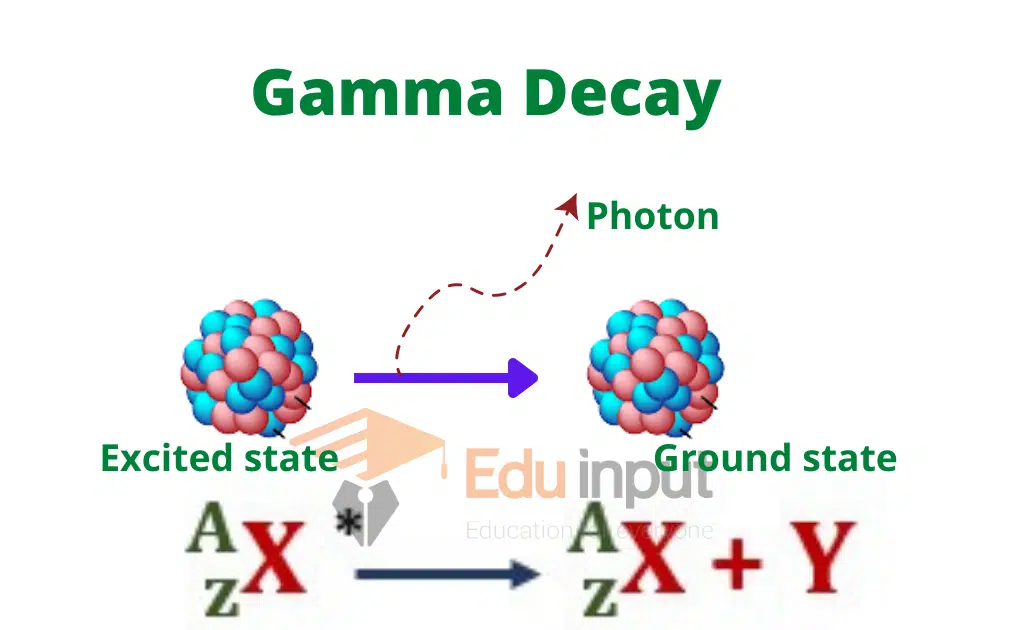
Here AZX*represents an excited nucleus while AZX shows the ground state of the nucleus.
Related FAQs
What is nuclear transmutation?
Nuclear transmutation is the conversion of one radioactive element into another radioactive element.
What is radioactive decay?
in a nuclear transmutation, the element changes into a new element. This phenomenon is called radioactive decay.
What is the daughter element?
The new element formed due to radioactive decay is called the daughter element.
What are the parent elements in radioactive decay?
The original element which takes part in radioactive decay is called the parent element.
How many types of radioactive decay?
There are three common types of radioactive decay
Alpha decay
Beta decay
Gamma decay





Leave a Reply