Heterotrophic And Special Mode Of Nutrition In Plants
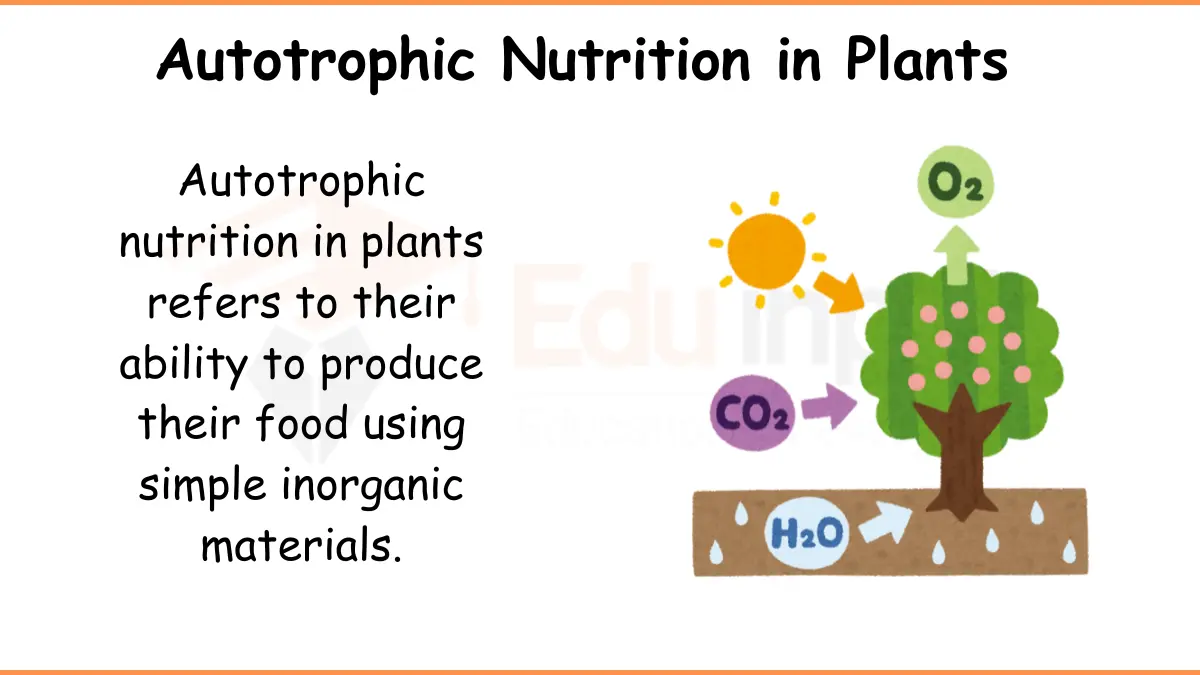
Plants, in contrast to animals, don’t need to get organic substances for their food, even though these materials make up most of their tissues. By holding solar energy in photosynthetic systems, they can create nutrients from carbon dioxide (CO2) and water.
Types Of Nutrition In Plants
Organisms can be divided into two groups based on their mode of nutrition:
a) Autotrophic nutrition: Autotrophic nutrition is the mode of nutrition in which organisms can synthesize their food from inorganic salts. Autotrophic organisms can exist in an exclusively inorganic environment. They synthesize their food in the form of sugars, lipids, and proteins from CO₂ and water.
b) Heterotrophic nutrition: Heterotrophic organisms rely on others for their sustenance. They cannot produce the food they need from simple inorganic nutrients and instead must take in molecules from the environment in the form of food.
Heterotrophic And Special Mode Of Nutrition In The Plants
The plants obtain their food from the air or water. But, there are following special methods of nutrition.
Saprophytic Nutrition
The feeding of dead and decaying matter is called saprophytic nutrition. This decaying matter includes dead leaves in the soil and rotting tree trunks.
a) The saprophytic plants produce extracellular enzymes. These enzymes digest and decay matter. Then the plants absorb the soluble products into their cells.
b) Some bacteria break down the proteins of dead plants and animals. They release nitrates. The roots of the plants absorb these nitrates. The plants synthesize new amino acids and proteins (translation) from these nitrates. So they play a role in the nitrogen cycle.
Parasitic Nutrition:
Feeding by living in or on other organisms belonging to different species is called parasitic nutrition. The parasites attach to the living hosts. The parasites penetrate their suckers into the conducting tissues of the host and absorb food.
Examples
a) Puccinia is a parasitic fungus. It destroys the wheat plant.
b) Dodder (Cuscuta) is a leafless plant. It lives as a twining parasite.
Symbiotic Nutrition:
It is mutual nutrition between organisms belonging to different species, living in association with one another. Some important examples are lichens, mycorrhizae, and root nodules.
1. Lichens:
The association between fungus and algae cells is called lichens. The algae make food for photosynthesis. The fungus supplies water and minerals. It also protects algae from desiccation.
2. Mycorrhizae:
The association between the fungus and roots of higher plants is called mycorrhizae. The fungus depends on the photosynthate (food formed from photosynthesis) of the plant. The benefit derived from the mycorrhiza plant is not properly understood. However, the plants with mycorrhiza association show better growth than those without this association.
Possibly, the fungus decomposes the organic material in the soil for the plants. It also provides water and minerals like phosphorus to plants.
3. Root Nodules :
The leguminous plants develop nodules on their roots These nodules contain nitrogen-fixing bacteria. The bacteria live on the plant material and fix atmospheric nitrogen. They convert this nitrogen into nitrates. These nitrates are used by plants.



Leave a Reply