What are Micromolecules?-Definition, Examples and Types
Micromolecules are relatively small molecules that are combined to form a Macromolecule. Micromolecules contain low molecular weight monomers. Micromolecules regulate different biological processes. Micromolecule is a molecule that is relatively smaller (than a macromolecule), or of low molecular weight that may regulate a biological process.
Examples Of Micromolecules
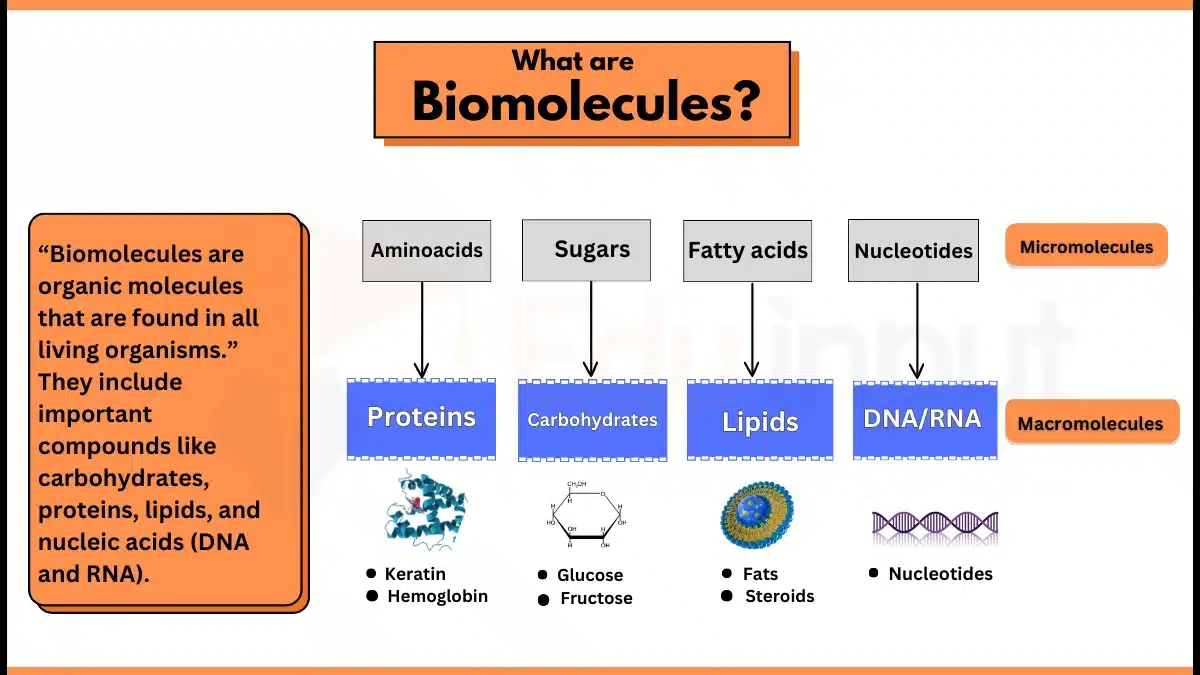
Examples of micromolecules are monomers (e.g. nucleotides, amino acids, monosaccharides, glycerol, and fatty acids) and inorganic compounds (e.g. water and minerals).
Amino acid micromolecules form proteins, fatty acids micromolecules form lipids, sugar micromolecules form glycerol and carbohydrates, and nucleobases micromolecules form DNA and RNA.
Types of Micromolecules
Here are some most common examples of micromolecules;
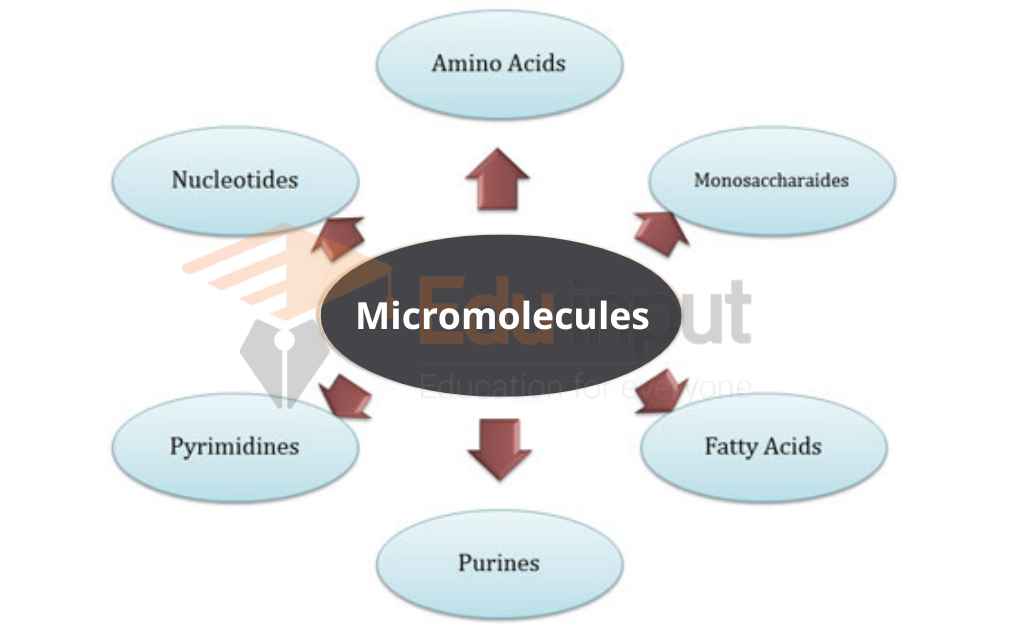
Amino Acids
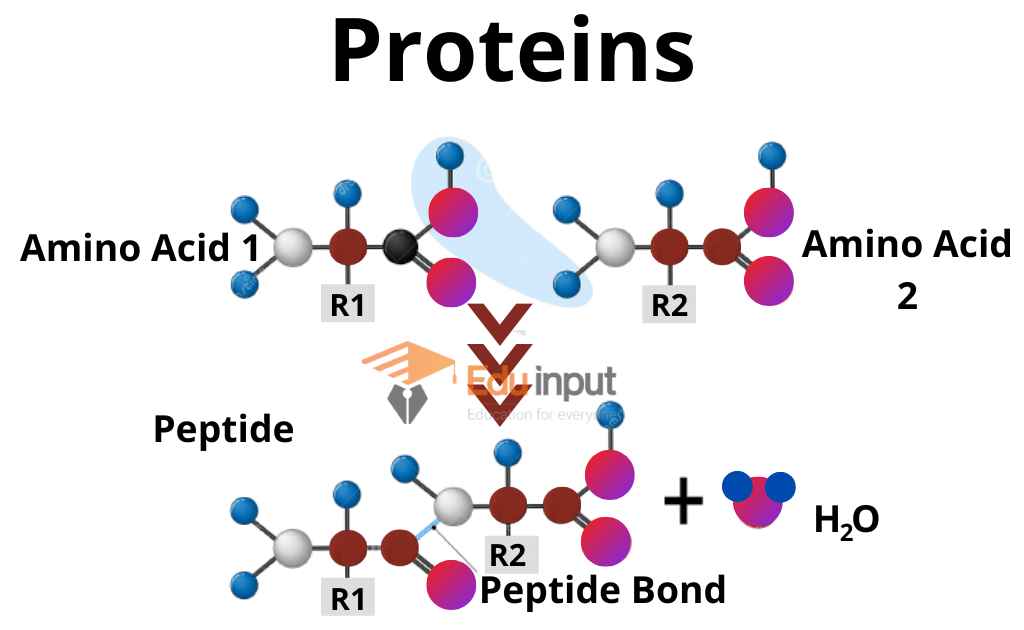
Amino acids are the building blocks of protein. Protein is the most abundant molecule in the body and is necessary for many processes including digestion, muscle contraction, hormone production, and immune system function. In addition to being a major structural component of cells, protein is also involved in cellular signaling and regulation. There are 20 different types of amino acids, each with their unique role in the body.
Nucleotides
Nucleotides are the smallest unit of DNA and RNA. They consist of a phosphate group, a 5-carbon sugar, and a nitrogenous base. Nucleotides are the basic units of nucleic acids and are the only components of DNA and RNA.
Vitamins
Vitamins are micronutrients that are essential to our bodies. Without these vitamins, we would not survive. A vitamin is a small organic compound that cannot be broken down by enzymes and therefore requires a cofactor to work properly. These cofactors are either minerals or specific proteins. Vitamins are categorized based on their chemical structure and physiological activity.
Minerals
Minerals are non-organic elements that are present in the earth’s crust. They are essential for the proper functioning of the human body and are commonly divided into two categories: macrominerals and trace minerals. Macro minerals are those that occur naturally in significant amounts in food and are generally consumed daily. Trace minerals are those that occur at low concentrations in food and are consumed less frequently.
Sugars
Sugars are the building blocks of carbohydrates. They include Glucose, Fructose, and Maltose.
Fructose is a monosaccharide (a single sugar molecule) that is present in fruits and vegetables. It is a simple carbohydrate that is easily digested and absorbed by the body.
Glucose is a disaccharide (two sugar molecules linked together). It is the primary sugar found in many foods and beverages. It is commonly known as blood sugar or dextrose.
Sucrose is a disaccharide (two sugar molecules linked) and is composed of glucose and fructose.
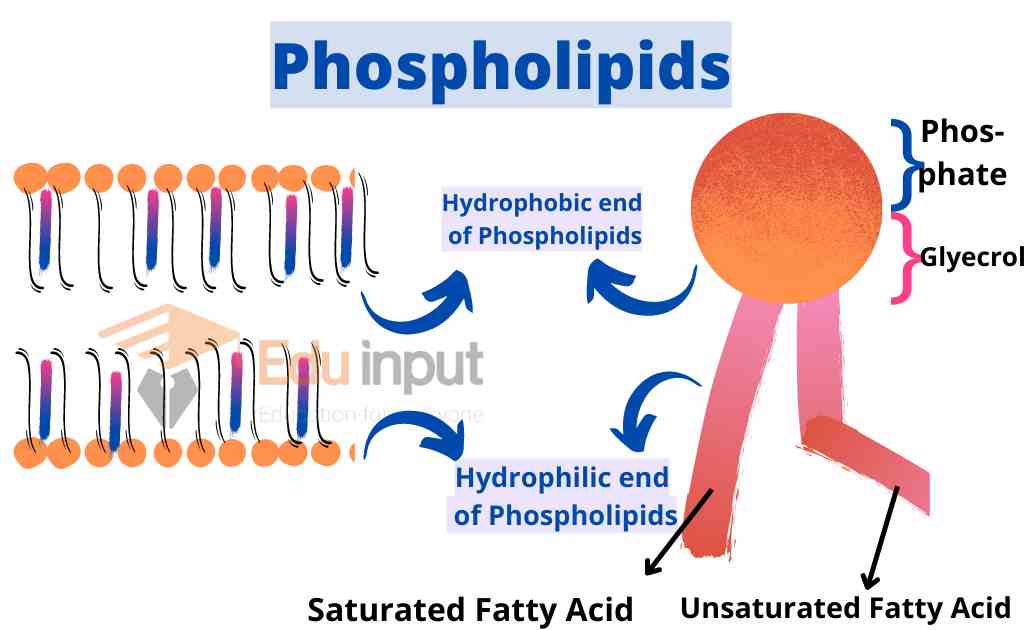
Fatty acids
Fatty acids are long-chain hydrocarbons. They are building blocks of lipids. Saturated fats are solid at room temperature and are not soluble in water. Monounsaturated fats have one double bond between two carbons and are liquid at room temperature. Polyunsaturated fats have several double bonds between carbons and are liquid under normal conditions.
Omega-3 fatty acids are polyunsaturated fats that are good for the heart. Omega-6 fatty acids are polyunsaturated that are bad for the heart.
What is a micromolecule in biology?
Micromolecule is a molecule of low molecular weight that combines to form macromolecules. They are called monomers, which after polymerization make macromolecules.
How many Micromolecules are there?
There are four major micromolecules;
Amino acids (monomers of protein)
Fatty acids (monomers of lipids)
Sugars (Monomers of carbohydrates)
Nucleotide (monomers of nucleic aicds)
Are lipids Micromolecules or macromolecules?
Lipids are macromolecule, but it is formed after the polymerization of a micromolecule, called fatty acids.
What are the building blocks of proteins?
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. There are 20 types of amino acids that form proteins in animal body.



Leave a Reply