10 Examples of Non-Spontaneous Reactions
The electrolysis of water, the formation of ozone, and the photosynthesis in plants are all examples of non-spontaneous reactions.
Also read: Examples of Spontaneous Reactions
Examples of Non-Spontaneous Reactions
Here are 10 examples of non-spontaneous reactions:
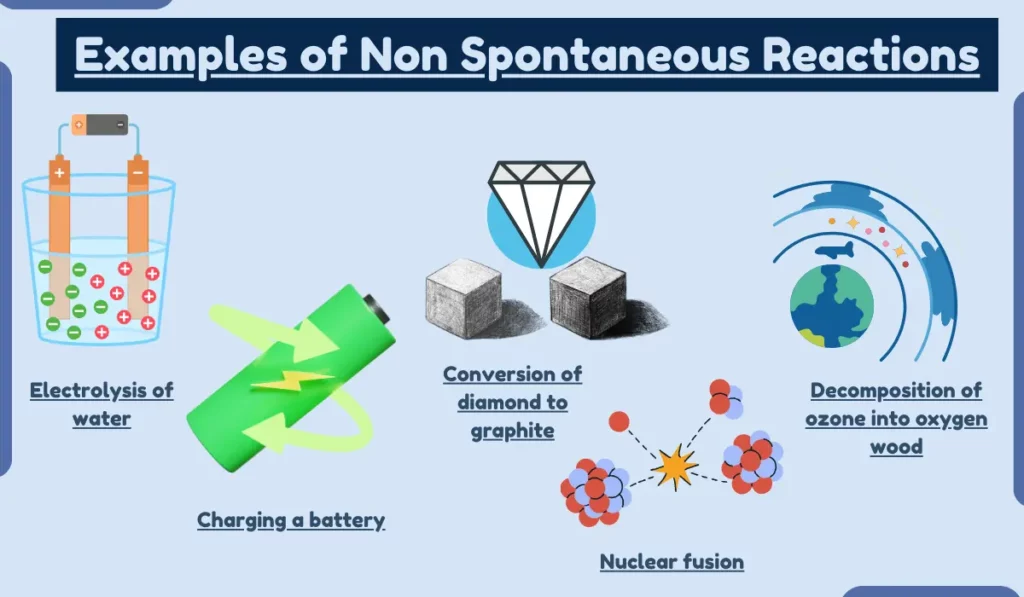
1: Electrolysis of water
Electrolysis of water is an example of a non-spontaneous reaction because it requires an external input of energy to drive the reaction. The energy from the electrical current is used to split the water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen gas.
Equation: 2H2O(l) + electrical energy -> 2H2(g) + O2(g)
2: Charging a battery
Charging a battery is a non-spontaneous reaction because it requires an external input of energy to drive the reaction. The energy from the electrical current is used to convert lead sulfate into lead and sulfuric acid.
Equation: PbSO4(s) + 2H2SO4(aq) + electrical energy —> Pb(s) + 2H2SO4(aq)
3: Dissolution of sodium chloride in water at high temperature
The dissolution of sodium chloride in water at high temperatures is a non-spontaneous reaction because it is Endothermic, meaning that it absorbs heat from the surroundings.
The energy required to break the ionic bonds in sodium chloride is greater than the energy released when the sodium and chloride ions become hydrated in water.
Equation: NaCl(s) —> Na+(aq) + Cl-(aq) + heat
Also read about Exothermic reactions
4: Formation of nitrogen monoxide from nitrogen and oxygen
The formation of nitrogen monoxide from nitrogen and oxygen is a non-spontaneous reaction because it is endothermic and has a negative entropy change.
The energy required to break the triple bond in nitrogen is greater than the energy released when the nitrogen and oxygen atoms form a double bond in nitrogen monoxide. Additionally, the formation of nitrogen monoxide from nitrogen and oxygen decreases the entropy of the system because it goes from two moles of gas (N2 and O2) to two moles of gas (2NO).
Equation: N2(g) + O2(g) —> 2NO(g) + heat
5: Decomposition of ozone into oxygen
The decomposition of ozone into oxygen is a non-spontaneous reaction because it is endothermic and has a negative entropy change.
The energy required to break the oxygen-oxygen bond in ozone is greater than the energy released when the ozone molecule dissociates into two oxygen molecules.
Additionally, the decomposition of ozone into oxygen decreases the entropy of the system because it goes from one mole of gas (O3) to two moles of gas (2O2).
Equation: 2O3(g) —> 3O2(g) + heat
6: Rusting of iron at low temperatures
The rusting of iron at low temperatures is a non-spontaneous reaction because it is too slow to be considered spontaneous. The activation energy required for the iron atoms to react with oxygen is too high at low temperatures.
Equation: Fe(s) + O2(g) —> Fe2O3(s)
7: Conversion of diamond to graphite
The conversion of diamond to graphite is a non-spontaneous reaction because it is too slow to be considered spontaneous. The activation energy required for the carbon atoms in the diamond to rearrange into graphite is too high at room temperature.
Equation: C(diamond) —> C(graphite)
8: Diffusion of gases against a concentration gradient
The diffusion of gases against a concentration gradient is a non-spontaneous reaction because it requires an external input of energy to drive the reaction.
The energy required to move gas molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration is greater than the energy released when the gas molecules become more evenly distributed.
Equation: NO2(g) —> NO2(g) (against a concentration gradient)
9: Osmosis against a water concentration gradient
Why: Osmosis against a water concentration gradient is a non-spontaneous reaction because it requires an external input of energy to drive the reaction.
The energy required to move water molecules from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration is greater than the energy released when the water molecules become more evenly distributed.
Equation: H2O(solution) -> H2O(pure) (against a water concentration gradient)
10: Nuclear fusion
Why: Nuclear fusion is a non-spontaneous reaction because it requires extremely high temperatures and pressures to occur. The energy required to overcome the repulsive forces between the nuclei of the atoms being fused is too high at room temperature and pressure.
Equation: 2H(g) -> He(g) + n(g) + energy
Also Read: Difference between Spontaneous and Non-Spontaneous Reactions
Difference Between Endothermic And Exothermic Reactions




Leave a Reply