Software as a Service (SaaS) – Advantages, examples, and Challenges
What is software as a service?
SaaS is a cloud computing model that enables users to access application software via the Internet on a subscription basis.
Software as a service definition
Instead of purchasing and installing software locally, users can access the application through a web browser, eliminating the need for complex installations or maintenance. There are many examples of browsers that can be used to access saas.

| Key points |
|---|
| 1. SaaS: a cloud-based model for accessing the software via subscription. 2. Benefits: convenience, cost-effectiveness, automatic updates. 3. Examples: CRM, project management, HRM, and email marketing. 4. Advantages over traditional software: scalability, integration, customization. 5. Implementation challenges: connectivity, data migration. 6. Future trends: AI integration, industry-specific solutions. 7. SaaS transforms the software landscape and gains popularity. |
In this digital age, where convenience and efficiency are paramount, SaaS offers a flexible and cost-effective alternative to traditional software models.
This article will explore the concept of SaaS, its benefits, examples of SaaS applications, advantages over traditional software, considerations for choosing SaaS, and implementation challenges.
History of Saas
1990s: Early days with Application Service Providers (ASPs) hosting basic software online. Salesforce emerged as a pioneer in 1999.
Mid-2000s: Faster internet allowed for more complex applications. “Cloud computing” has become the buzzword.
In the late 2000s, big tech players like Google and Microsoft joined the cloud game with web-based apps.
2010s: Businesses shift from on-premise software to cloud-based SaaS, focusing on integration, security, and AI.
Early 2020s: The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of SaaS due to remote work needs.
2023 and beyond: SaaS will become essential for businesses, with solutions for almost every sector. It will be a key player in digital transformation.
SAAS Architecture
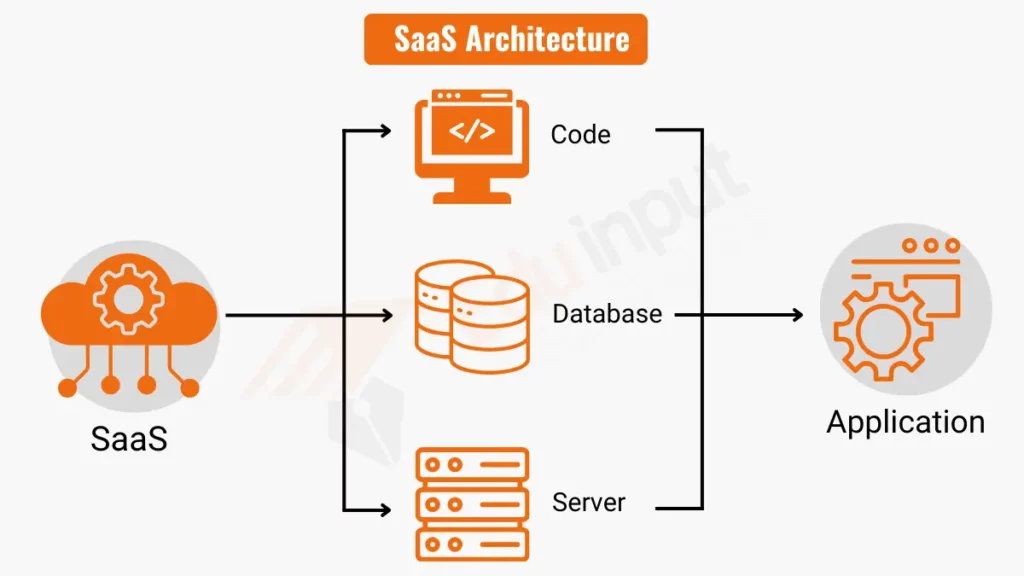
SaaS architecture represents a sophisticated yet user-friendly configuration that provides software solutions via the cloud. It starts with application code, which is the heart of the SaaS offering and enables dynamic and robust software functionality.
This code interacts seamlessly with a database, securely storing and managing all user data. The server plays a crucial role as the architecture’s powerhouse, handling requests and delivering services efficiently to users.
Together, these components form integral parts of the SaaS ecosystem, working in unison to ensure that software services are delivered smoothly, securely, and scalably. This architecture supports continuous updates and maintenance without disrupting the user experience, illustrating the practical elegance of SaaS solutions.”
How does SaaS work?
In the SaaS model, the software provider takes responsibility for hosting, maintaining, and securing the application infrastructure.
Users can sign up for the service, log in, and use the software immediately. The provider handles software updates, security patches, and data backups, relieving users of managing these aspects themselves.
Examples of SaaS Applications
SaaS has gained popularity across various industries, and many applications are available. Here are some common examples:

- Salesforce as Saas
- Slack as Saas
- Dropbox as Saas
- HubSpot as Saas
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) as Saas
- Netflix as Saas
- Shopify as Saas
- Zendesk as Saas
- Google Docs as Saas
SaaS vs. IaaS vs. PaaS
In the cloud computing landscape, three primary service models exist: Software as a Service (SaaS), Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), and Platform as a Service (PaaS). Each model offers different levels of control, flexibility, and management, catering to various business needs.
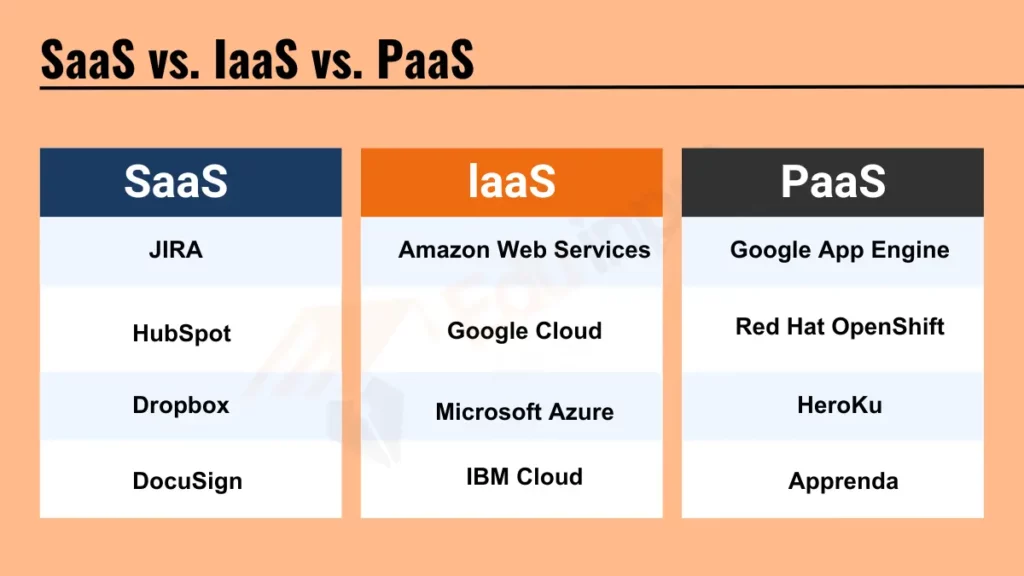
- SaaS (Software as a Service) is the most inclusive and user-friendly model, providing customers with ready-to-use, fully functional applications over the Internet. Examples include JIRA for project management, HubSpot for marketing automation, Dropbox for cloud storage, and DocuSign for electronic agreements.
- IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) offers a virtualized computing infrastructure managed over the Internet. It is a foundational layer providing users with resources such as virtual machines, networks, and storage. Leading IaaS providers are Amazon Web Services, Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, and IBM Cloud.
- PaaS (Platform as a Service) provides customers with a platform allowing them to develop, run, and manage applications without the complexity of building and maintaining the underlying infrastructure. Examples of PaaS include Google App Engine, Red Hat OpenShift, Heroku, and Apprenda.
Advantages of SaaS over Traditional Software
There are many advantages of using SaaS, which is given below:
Cost-effectiveness
SaaS eliminates the need for upfront hardware and software investments. Users can subscribe to a SaaS application at a predictable recurring cost, avoiding the expenses associated with purchasing licenses, servers, and maintenance.
Scalability and flexibility
SaaS applications are designed to be scalable, allowing users to adjust their subscription plans as their needs change easily. Whether a business expands or contracts, SaaS provides the flexibility to adapt software usage accordingly.
Automatic updates and maintenance
In the SaaS model, software providers handle updates and maintenance tasks. This ensures that users can always access the latest features and security patches without requiring manual installations or disruptions.
Security and data privacy
Since SaaS applications store sensitive data in the cloud, assessing the provider’s security measures is crucial. Look for industry-standard encryption, data backup protocols, and compliance with data protection regulations.
Integration capabilities
Consider how well the SaaS application integrates with other software or systems your business uses. Seamless integration can enhance productivity and streamline workflows.
Customization options
Evaluate the level of customization offered by the SaaS provider. Depending on your specific needs, you may require the ability to tailor the application to match your business processes and branding.
Vendor reputation and support
Research the SaaS provider’s reputation and track record. Read reviews, seek recommendations, and inquire about their customer support responsiveness. A reliable vendor with excellent support can ensure a smooth and satisfactory user experience.
Challenges of Implementing SaaS
SaaS offers many benefits, but there are also many challenges, which are given below:
Internet connectivity and reliability
SaaS applications heavily rely on internet connectivity. If the internet connection is unstable or slow, it can hinder productivity and access to critical software functionalities.
Data migration and integration
Migrating data from existing systems to a new SaaS application can be complex. Ensure that proper data migration tools and support are available to transfer your data without disruptions seamlessly.
Future Trends in SaaS
SaaS continues to evolve, and several trends shape its future:
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in SaaS
AI and machine learning are being integrated into SaaS applications, offering advanced analytics, personalized experiences, and automation of repetitive tasks.
Edge computing and SaaS
Edge computing, where data processing occurs closer to the source, is gaining traction in SaaS. This enables faster response times, reduced latency, and enhanced data privacy.
Industry-specific SaaS solutions
As businesses seek tailored solutions, industry-specific SaaS applications are emerging. These cater to the unique needs and regulations of specific sectors and provide targeted functionalities.
Software as a Service (SaaS) has transformed the software landscape by providing accessible, scalable, and cost-effective solutions. With its numerous benefits, including flexibility, cost savings, and automatic updates, SaaS continues to gain popularity across industries. However, carefully considering factors such as security, integration capabilities, and customization options is necessary when choosing a SaaS provider.
Despite challenges such as internet connectivity and data migration, the future of SaaS looks promising, with trends like AI integration and industry-specific solutions shaping its evolution.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an example of SaaS?
Examples of SaaS applications include Salesforce, HubSpot, Microsoft Office 365, and Dropbox.
Is Netflix a SaaS?
Yes, Netflix is considered a SaaS platform as it provides streaming services to users through a subscription model.
Is Amazon a SaaS?
Amazon provides various services, including web hosting (Amazon Web Services) and cloud-based solutions (Amazon Web Services), which can be categorized as SaaS.
Is Facebook a SaaS or PaaS?
Facebook is primarily a social media platform and can be classified as a SaaS application.
Is Uber a SaaS or PaaS?
Uber can be categorized as a SaaS platform since it provides transportation services through a mobile application accessed by users via the Internet.





Leave a Reply