What is Biochemistry-history, scope, Types, applications
Biochemistry definition
Biochemistry is the study of chemical components and the chemical processes in living organisms.
Biochemistry is a branch of chemistry that deals with the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. It is a diverse and interdisciplinary field that combines elements of biology, chemistry, physics, and mathematics. In this article, we will explore the history, scope, types, and applications of biochemistry.
Biochemistry can explain processes like photosynthesis, respiration, digestion, and muscle contraction.

History of Biochemistry
The history of biochemistry dates back to the 19th century when chemists began to study the chemical processes occurring within living organisms.
In 1828, Friedrich Wohler synthesized urea, a substance found in urine, and demonstrated that organic compounds could be synthesized from inorganic materials.
This led to the concept of vitalism, which suggested that living organisms were fundamentally different from non-living matter.
In the late 19th century, the discovery of enzymes and their role in catalyzing biological reactions led to a more mechanistic view of biochemistry.
In the early 20th century, the discovery of DNA and the elucidation of its structure and function marked the beginning of the molecular biology revolution, which transformed the field of biochemistry.
Scope of Biochemistry
The scope of biochemistry is vast, encompassing many different fields of study. Some of the major fields of study within biochemistry include:
Molecular Biology
Molecular biology is the study of the molecular basis of biological activity. It involves the study of DNA, RNA, and proteins, and their interactions within the cell.
Genetics
Genetics is the study of heredity and variation in living organisms. It involves the study of genes, their structure, and function, and how they are transmitted from one generation to the next.
Immunology
Immunology is the study of the immune system, which is responsible for defending the body against infection and disease. It involves the study of the structure and function of the immune system, as well as the development of vaccines and other therapies to combat disease.
Microbiology
Microbiology is the study of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. It involves the study of their structure, function, and interactions with other organisms.
Physiology
Physiology is the study of the functions of living organisms and their parts. It involves the study of how living organisms carry out their vital functions, such as respiration, circulation, digestion, and reproduction.
Types of Biochemistry
Biochemistry can be divided into several sub-disciplines or types, each with its own focus and applications. Some of the major types of biochemistry include:
Structural Biochemistry
Structural biochemistry is the study of the three-dimensional structure of biological molecules such as proteins, nucleic acids, and carbohydrates.
It involves the use of techniques such as X-ray crystallography and NMR spectroscopy to determine the structure of these molecules and understand how their structure relates to their function.
Metabolic Biochemistry
Metabolic biochemistry is the study of the chemical reactions that occur within living cells, which are collectively known as metabolism. It involves the study of the pathways by which cells convert nutrients into energy and other biomolecules necessary for cellular function.
Nutritional Biochemistry
Nutritional biochemistry is the study of the interaction between nutrients and the human body. It involves the study of how nutrients are metabolized and used by the body, as well as the role of nutrients in disease prevention and treatment.
Enzymology
Enzymology is the study of enzymes, which are biological catalysts that accelerate chemical reactions within living organisms. It involves the study of enzyme structure, function, and regulation, as well as the application of enzymes in industrial processes.
Biotechnology
Biotechnology is the use of living organisms or their components to produce useful products or processes. It involves the application of biochemistry and other life sciences to develop new technologies for medicine, agriculture, and industry.
Clinical Biochemistry
Clinical biochemistry is the application of biochemistry to the diagnosis and management of disease. It involves the use of biochemical tests to assess the status of various physiological systems, such as the liver, kidney, and heart.
Applications of Biochemistry
Biochemistry has numerous applications in various fields of science and technology. Some of the major applications of biochemistry include:
Medicine
Biochemistry plays a critical role in medicine, from drug discovery to disease diagnosis and treatment. Biochemical techniques are used to identify and develop new drugs, monitor disease progression, and assess the effectiveness of treatments.
Agriculture
Biochemistry is important in agriculture, where it is used to improve crop yields, develop disease-resistant plants, and improve the quality and safety of food products.
Food Industry
Biochemistry is used extensively in the food industry, where it is used to develop new food products, improve the nutritional content of foods, and ensure the safety of food products.
Environmental Science
Biochemistry plays a role in environmental science, where it is used to study the biochemical processes involved in biodegradation, pollution, and ecosystem dynamics.
Biochemistry is a vast and diverse field that has numerous applications in many different areas of science and technology.
From the study of basic biological processes to the development of new medical treatments and agricultural technologies, biochemistry plays a critical role in advancing our understanding of the living world.
How does Biochemistry explain Chemical composition of Organisms?
Biochemistry investigates the chemical composition and processes occurring within living organisms. It provides a detailed understanding of how the chemical building blocks and interactions of molecules contribute to the structure and function of biological systems.
All living things are made up of certain chemical compounds. There are two types of molecules, Organic and inorganic molecules.
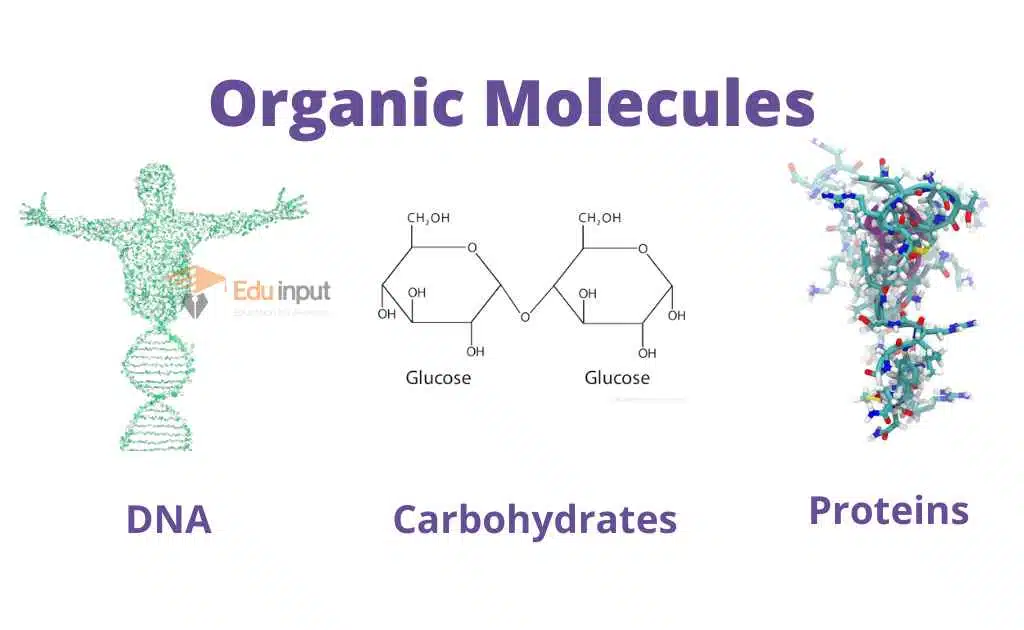
The molecules present in the animals are called organic molecules. The important groups of organic molecules in animals include carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleotides, and nucleic acids.
Organic Molecules
They contain carbon atoms. The characteristics of organic molecules depend on the properties of carbon. Covalent bonding enables carbon to bond with other carbon atoms so it forms chains and rings of different lengths and configurations.
The organic molecules containing only carbon and hydrogen are called Hydrocarbons.
Most organic compounds in living organisms are carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids.
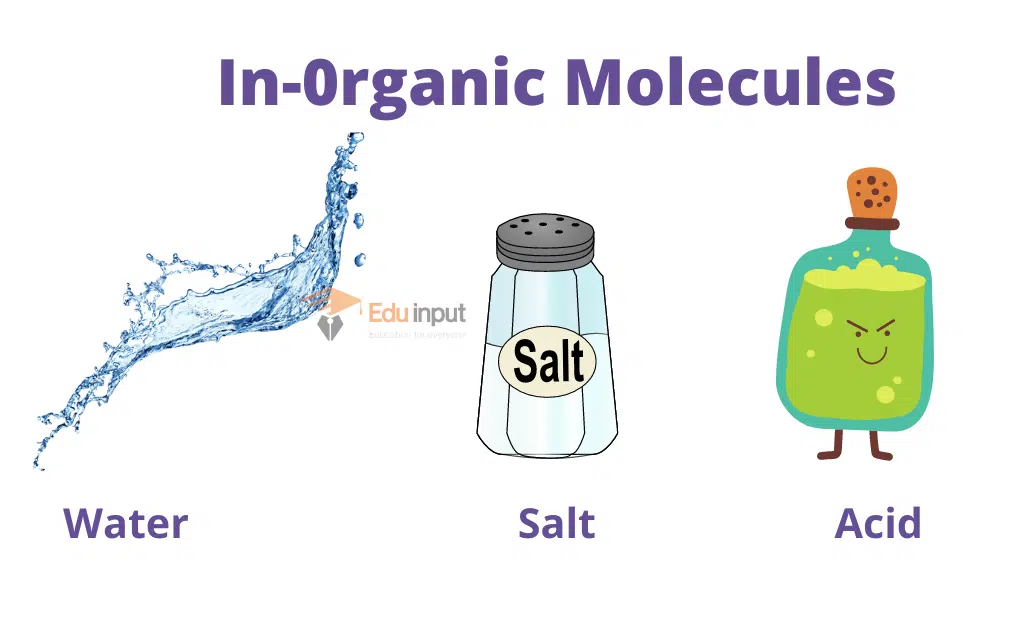
Inorganic Molecules
They lack carbon atoms. A few simple molecules containing carbon are inorganic. Its example is CO₂. Inorganic substances are water, Carbon dioxide, acids, bases, and salts.
Chemical Composition of Bacterial and Mammalian cell
Bacteria and Mammals have different percentages of different chemicals.
| No. | Chemical Components | % weight of Bacterial cell | % weight of Mammalian cell |
| 1 | Water | 70 | 70 |
| 2 | Proteins | 15 | 18 |
| 3 | Carbohydrates | 3 | 4 |
| 4 | Lipids | 2 | 3 |
| 5 | DNA | 1 | 0.25 |
| 6 | RNA | 6 | 1.1 |
| 7 | Other organic molecules | 2 | 2 |
| 8 | Inorganic ions | 1 | 1 |
Chemical Activity in Organism’s Body
The survival of an organism depends upon chemical activities. The organisms take chemicals from their environment. They make chemicals in their cells from these chemicals. Thus the cells of every organism constantly take new substances.
They change these substances chemically in various ways. They use them in building cellular materials and obtaining energy for their need.
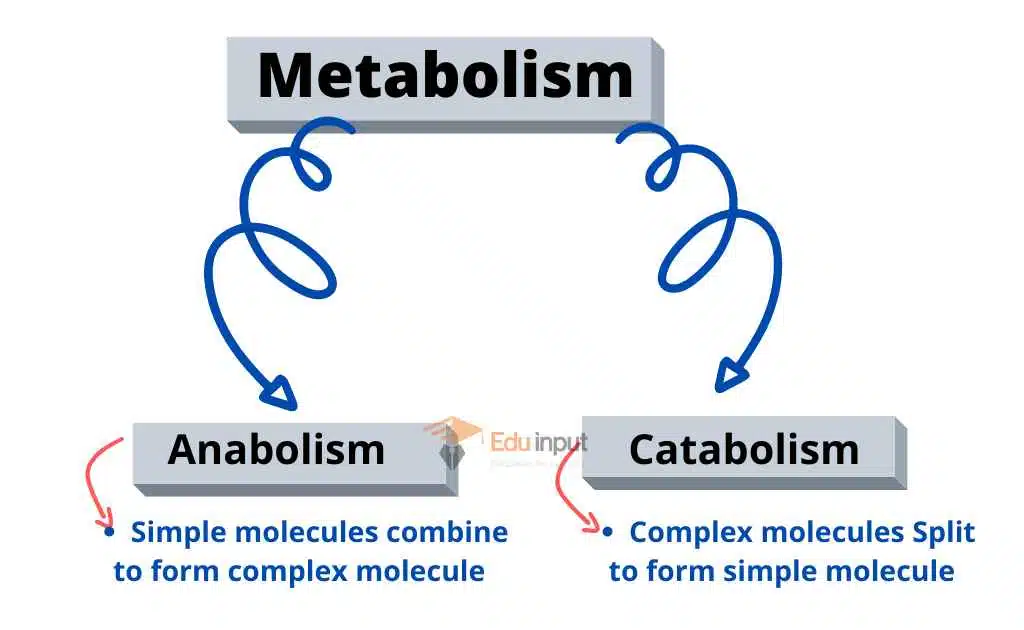
Metabolism
All the reactions taking place in the cells are collectively called metabolisms.
Metabolism is of two types:
1- Anabolism
The reactions in which simple molecules combine to form complex substances are called anabolic reactions.
Biochemistry explains these processes. Anabolic reactions need energy. Energy is released during the breakdown of complex molecules into simple molecules. An example of an anabolic reaction is photosynthesis.
2- Catabolism
The reactions in which complex molecules are broken into simple molecules are called catabolic reactions.
Energy is released during catabolic reactions.
Interconversions of Molecules
Anabolic and catabolic reactions occur hand in hand in cells. Complex molecules are broken down into small molecules. Then these small molecules are reused to form new complex molecules. Therefore, interconversions of carbohydrates, proteins, and
lipids occur continuously in living cells. It is an example of co-coordinated catabolic and anabolic activities.
Related FAQs
What is Biochemistry?
Biochemistry is the study of chemical components and the chemical processes in living organisms.
What is an organism made up of?
All living things are made up of certain chemical compounds. The molecules present in the animals are called organic molecules. The important groups of organic molecules in animals include carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleotides, and nucleic acids.
What is the difference between biochemistry and molecular biology?
Biochemistry focuses on the study of chemical processes within living organisms, while molecular biology focuses on the study of the molecular basis of biological activity.
What are some of the major fields of study within biochemistry?
Some of the major fields of study within biochemistry include molecular biology, genetics, immunology, microbiology, physiology, and pharmacology.
What are some of the major fields of study within biochemistry?
Some of the major fields of study within biochemistry include molecular biology, genetics, immunology, microbiology, physiology, and pharmacology.
What is the role of biochemistry in medicine?
Biochemistry plays a critical role in medicine, from drug discovery to disease diagnosis and treatment. Biochemical techniques are used to identify and develop new drugs, monitor disease progression, and assess the effectiveness of treatments.




Leave a Reply