What is Biology?
Biology is the scientific study of life. The word Biology is derived from two Greek words, “bios” and “logos” which means “thought or reasoning” and “life” respectively.
Biology is essential to understanding and appreciating nature, and thus to understanding and appreciating it. Understanding living organisms helps you to understand human problems regarding health, food, the environment, and so on.

Who is the Father of Biology?
Aristotle is called the Father of biology. Aristotle was a great philosopher and a polymath during the classical period in Ancient Greece.
Aristotle’s work on zoology is considered to be the foundation of modern biology, because of his use of systematic classification and his use of physiology to uncover relationships between animals.
In addition, Charles Darwin is known as the Father of Modern Biology.
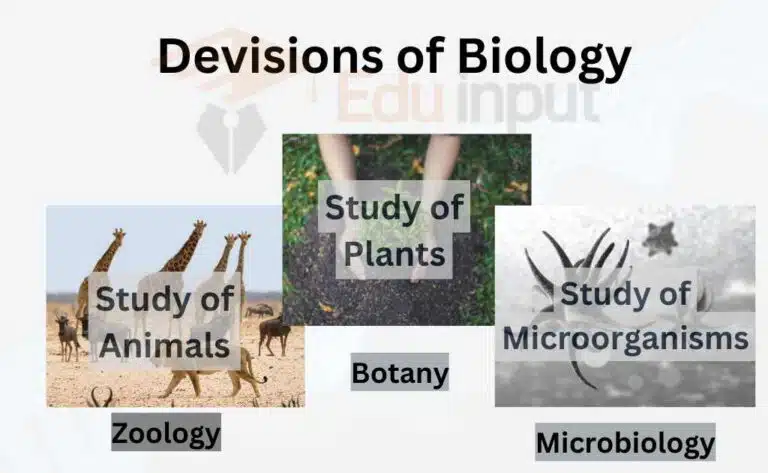
Divisions of biology
There are three major divisions of biology:
Zoology
The biology division, particularly dealing with the study of animals, is called zoology.
Botany
The division of biology particularly dealing with the study of plants is called botany.
Microbiology
The biology division that deals with studying microorganisms such as bacteria and viruses is called microbiology.
Branches of biology
To study all the aspects of life, these divisions are further divided into different branches as defined below.
Morphology
This branch deals with the study of the form and structure of living organisms.
Anatomy
Anatomy is a branch of biology that involves the study of internal structure i.e Anatomy of Human Ear.
Histology
The microscopic study of tissues and organs of living organisms is known as histology.
Molecular Biology (Biochemistry)
This branch deals with the study of biological molecules such as proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids (DNA and RNA).
Histology
The microscopic study of tissues is called histology.
Cell Biology
The study of the cell (i.e Animal and Plant Cells), its cellular structures, and its functions is called cell biology.
Physiology
The study of the functions of different parts of living organisms is called physiology.
Genetics
The study of genes (present in Hereditary material DNA and Chromosomes) and their roles in inheritance is called genetics.
Embryology
It is the study of the development of an embryo into a new individual.
Taxonomy
Taxonomy is the study of the names and classifications of organisms based on their features and ancestors.
Paleontology
It is the study of fossils, which are the remains of extinct organisms.
Environmental Biology
It deals with the study of the interactions between organisms and their environment.
Socio-Biology
This branch deals with the study of the social behavior of the animals that make societies.
Parasitology
The study of parasites is referred to as parasitology.
Biotechnology
Biotechnology is the science of developing or creating products using biological systems, living organisms, or parts of this, for the betterment of mankind.
Immunology
It is the study of the immune system of animals, which defends the body (like leukocytes).
Entomology
The study of insects is what entomology is all about.
Pharmacology
The study of drugs and their effects on the systems of the human body is called pharmacology.
Ecology
Ecology is the study of how all of the creatures that live in the world depend on each other and their surroundings. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community level, and Ecosystem levels.
Relationship of biology to other sciences
You will never find a single discipline that is the whole science. Each branch of science has relationships with all the others. For example, biologists sometimes study the process of movement in animals by studying the laws of motion in physics.
Principles are often the same across different disciplines, but rules are specific to a discipline.
Biophysics
Biophysics is a combination of physics and biology. It involves the principles of physics, that apply to all biological processes.
For example, if we look at an animal, we can see that it uses its limbs (hands and feet) like levers.
Biomathematics
Biomathematics covers the study of biological processes using mathematical techniques and tools. It helps to analyze data from experiments performed by scientists, using the rules of mathematics and statistics.
Biogeography
The study of the occurrence and distribution of different species of living organisms in other geographical regions of the world is called biogeography.
The characteristics of living organisms are determined by applying the knowledge of the characteristics of that particular region.
Bioeconomics
Bioeconomics studies organisms from an economical perspective. The yield of wheat can be calculated using bioeconomics, and that’s what the benefits and losses are based on.
Biochemistry
The study of the chemistry of compounds and processes in living organisms is called biochemistry. For example, in the study of the basic metabolism of photosynthesis and respiration, knowledge of chemistry is needed.
It also involves the study of chemical substances present in body living organisms such as Hormones, or Vitamins.
Scope of biology
We need the knowledge and skills to be successful in the future. To comprehend several sciences and scientific research projects, students need to have an accurate understanding of biology. Any career will benefit from it.

A student of biology can take these career paths:
Medicine/surgery: one can join the medical field i.e medicine/surgery or physician after joining the course of MBBS. This course is offered after 12 years of education with a premedical background that involves biology as a major.
Fisheries: Fisheries is the study of fish, to enhance the quality and quantity of fishes. Fisheries can be joined after 12 years of education, and a specialization in zoology in zoology. Fisheries professionals can also join govt. Department of fisheries or wildlife.
Agriculture: It deals with agriculture, and helps in enhancing food sources. An agriculture professional works to increase the quality and yield of crops. Many courses are being offered in agriculture, that can be joined after 12 years of education, primarily with biology as a major.
Animal husbandry: It deals with the ways concerned with the care, protection, and breeding of livestock. Its course can be adopted after 12 years of education with biology as a major.
Horticulture: A horticulturist works for the betterment of gardening, and takes care of the different varieties of plants. People with a biology background can easily join the course after higher secondary education.
Farming: Farming is the field concerned with the development and maintenance of cattle, fish, or poultry farms. A student who has completed professional courses in agriculture, animal husbandry, or fisheries can join it.
Forestry: Foresters take care of existing forests and design new plans to increase the forests. They make plans for the government to grow new plants. This profession can be joined after a degree in zoology, biology, botany, or a particular course in forestry.
Biotechnology: Biotechnologists work for the betterment of humans by using biotechnology techniques like genetic engineering. Courses are being offered in biotechnology and genetics after higher secondary education.
Biology is the scientific study of life. The word Biology is derived from two Greek words, “bios” and “logos” which means “thought or reasoning” and “life” respectively.
Biology is essential to understanding and appreciating nature, and thus to understanding and appreciating it. Understanding living organisms helps you to understand human problems regarding health, food, the environment, and so on.
Topic Wise Biology Articles
Difference Between Articles in Biology
Difference between Diffusion and Facilitated Diffusion
Difference Between Insect and Pest
Difference Between Hand and Arm
Difference Between Inductive And Deductive Reasoning
Difference Between Fermentation and Rotting
Differences between Tactic Movement and Tropic Movement
Difference Between Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration
Difference Between Autotrophs and Heterotrophs
Difference Between Diffusion and Osmosis
Difference Between Food Chain and Food Web
Difference Between Transcription And Translation
Difference Between Genotype and Phenotype
Difference Between Antibiotics and Vaccines
Difference Between Chromosomes and Genes
Differences Between DNA And RNA
Differences Between Monocots And Dicots
Difference Between Gram Positive and Gram Negative Bacteria
Difference between Archaea and Bacteria
Difference Between RBCs and WBCs
Difference Between Radial and Bilateral Symmetry
Differences Between Chemosynthesis And Photosynthesis
Difference Between Inbreeding And Outbreeding
Difference Between C3 and C4 Plants
Difference Between Gametophytes And Sporophytes
Differences Between Fibrous Proteins And Globular Proteins
Differences Between Antigens And Antibodies
Differences Between Dominant And Recessive Traits
Difference Between Innate Immunity And Adaptive Immunity
Differences Between Variation And Mutation
Differences Between Taxonomy And Phylogeny
Difference Between Invertebrates And Vertebrates
Difference Between Autosomes and Sex Chromosomes
Differences Between Catabolism And Anabolism
Differences Between Endotherm And Ectotherm
Difference between Enzymes and Hormones
Difference Between Tundra and Desert Biome
Difference Between Predation and Parasitism
Differences Between Instinctive Behavior And Learning Behavior
Difference Between Bone And Cartilage
Difference Between The Nervous System Of Hydra And Planarian
Difference Between Photosynthesis And Respiration
Difference Between Diploblastic Organization And Triploblastic Organization
Difference Between Arteries And Veins
Difference Between Pathogen And Parasites
Difference Between Cerebellum And Cerebrum
Difference between Algae and Fungi
Difference Between Bryophytes And Pteridophytes
Difference Between Pteridophytes And Gymnosperms
Difference Between Cell Wall And Cell Membrane
Difference Between Bacteria And Cyanobacteria
Difference Between Bacteria And Algae
Difference Between Viruses and Bacteria
Difference Between Cofactor and Coenzyme
Difference Between Animal and Plant Cell
Bioenergetics
What are light-Dependent Reactions? | Occurrence of Light-Dependent Reactions
Light Independent Reactions | Calvin Cycle
Electron Transport Chain | Step-by-Step guide to Process Of Electron Transport Chain
ATP- Cell’s Energy Currency – Structure and Functions | Mechanism of Energy Transfer by ATP
ATP Synthesis Pathway | Substrate Level Phosphorylation | Mechanism of Chemiosmosis
Rubisco (Ribulose Bisphosphate Carboxylase) – Role in Photorespiration
What is Gluconeogenesis? – Importance and Regulation
What is Chlorophyll?-Composition and Structure
What is Glucose?-Glucose in Plants, Animals, and Humans
What is Glycolysis? | Steps of Glycolysis
Photosynthesis-Process, Factors, Formula, Adaptations
How Are Photosynthesis And Cellular Respiration Related?
How Does The Process Of Photosynthesis Affect The Atmosphere?
Variety Of Life
General Structure of Viruses- Viral Capsid, Envelop and Genome
Reproduction in Viruses | Step-by-Step Guide to Viral Replication
Tobacco Mosaic Virus (TMV) – Structure and Transmission Mechanism
Bacteriophage-Structure, Types, and Replication
What Is Biological Classification?-Basis And Units
Kingdom Animalia
Invertebrates-Classification of Invertebrates
Mammalia-Characteristics and Classification of Mammals
Modes of Development in Mammals | Monotremes, Marsupials and Eutherian Mammals
Invertebrate Coelomic Fluid And Hemolymph
What is Coelomic Fluid?-Coelomates, Pseudocoelomates, And Coelomates
Phylum Porifera-Characteristics, Examples, and Importance
Vertebrates (Definition, Evolution, Characteristics, Classification, Systems, and Examples
Examples of Vertebrates (Name, Habitat, Nutrition, & Pictures)
Kingdom Plantae
Reproduction In Bryophytes-Vegetative, Asexual and Sexual Reproduction
What are Bryophytes?-Occurrence, General Structure and Life Cycle
What is Seed?-Definition, Structure, and Nature of Seed
Alternation Of Generations In Bryophytes | Significance of Alternation of Generation
Evolution of the Leaf- Shape, Texture, and Veination
Kingdom Protista (Or Protoctista)
Algae-Occurrence, Cell Structure, Pigments, and Reproduction
What is Cilia?-Structure, Types, and Functions
What is the Economic Importance of Lichens?
Economic Importance Of Algae | Beneficial Effects of Algae
Reproduction In Algae-Vegetative, Sexual, and Asexual Reproduction
Kingdom Prokaryotes (Monera)
What is Bacteria? – Classification, Characteristics, Types, Structure, and Shapes
Classification of Bacteria Based on Shapes
Gram Staining Technique | Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Bacteria
Flagella-The Locomotory Organ of Bacteria
Protozoa-General Structure, Characteristics, and Classification
Cyanobacteria – Characteristics, Structure, Reproduction, and Classification
What is Binary Fission?-Definition, Types and Mechanism
What is Transduction in Bacteria?-Mechanism and Types
Bacterial Pathogenicity | Classification of Pathogenic Bacteria
Internal Anatomy of Bacterial Cell
Classification Of Bacteria-Definition and Examples
What is Bacterial Conjugation?-Definition, Process, and Benefits
What are Antibiotics in Biology?-Categories, Effects, and Precautions
Nutrition In Bacteria | Methods Of Nutrition In Bacteria
What are the Phases Of Growth In Bacteria?
Evolution
The Theory Of Evolution By Natural Selection
What Is Lamarckism?-Lamarck Theory, Significance, And Examples
What Is Genetic Drift?-Definition, Cases, and Examples
Recapitulation Theory Or Biogenetic Law of Ernst Haeckel
Role of Genetic Engineering in Agriculture
Molecular Evolution and Mosaic Evolution-An Overview
What are Endangered Species?-Reasons Of The Extinction Of Species
Support and Movement
Epithelial Tissues-Structure, Types, And Functions
What Are Animal Tissues?-Types And Functions
What Are Muscular Tissues?-Properties, Composition, Types, And Functions
What Are Tissues?-History, Types, And Examples
Connective Tissues-Definition, Structure, Types, Functions, and Examples
What Is Cartilage?-Composition, Types, And Functions
Appendicular Skeleton | Blood Supply in Appendicular Skeleton
Genetic Engineering of Plants-Applications And Advantages
Skeletal System-Definition, Composition, and Functions
Deformities of Skeleton-Causes and Examples
Support In Plants-Cells Involved In Support
What is Growth in Plants?-Process and Types of Growth
What Is Locomotion of Soft-Bodied Invertebrates?
What is Ciliary Movement?-Ciliary movement in Protozoans and flatworms
Non-Muscular Movement-Definition and Types | Amoeboid Movement
Bone or Osseous Tissue-Definition, Parts, Composition, and Functions
Support And Movement In Animals | Types Of Skeleton
Tropic and Nastic Movement in Plants | Paratonic Movement in Plants
Tactic Movement in Plants-Definition and Examples
Turgor and Growth Movement in Plants | Autonomic Movement in Plants
How the cross-bridges are controlled?
Introduction To Muscles | Functions, and Types of Muscles
Sliding Filament Model of Muscle Contraction
Biotechnology
10 Applications of Biotechnology in Medicine
Difference Between Synthetic Biology and Genetic Engineering
What is Fermentation?-Steps, Types, And Examples
What Type Of Organism Can Carry Out Alcoholic Fermentation?
When Does Fermentation Takes Place In Your Muscle Cells?
What is Bioremediation?-Agents, Types And Techniques
What Are Edible Vaccines?-Advantages And Limitations
Real World Applications of Biotechnology
Recombinant Insulin-How Is It Produced?
Genetic Engineering of Plants-Applications And Advantages
The Human Genome Project-Goals, Methods, and Applications
DNA Sequencing-Methods and ApplicationsBiocontrol-Agents, Strategies, and Disadvantages
Homeostasis
What is Homeostasis?-Definition, Objectives, and Levels of Homeostasis
Homeostasis Regulation-Living and Physical Control System
Excretion in Plants-Excretory Products and Organs
Mechanism of Thermoregulation in Mammals
What is Urea Cycle? (History, Reactions, Enzymes, and Steps)
Nature Of Excretory Products In Relation To Habitat
Electrolyte Balance In Human Body
How Homeostasis Relates To Both Healthy Body Functions And Disorders?
How Homeostasis Is affected By pH And Osmosis?
Biological Molecules
Carbohydrates | Classification of Carbohydrates
What are Lipids?-Discovery, Sources, Classification, and Importance
What are Proteins? | Brief Description of Amino Acids and Peptide Bond
Nucleic Acid- Discovery and Types Of Nucleic Acid
What is Biochemistry-history, scope, Types, applications
What is RNA (Ribonucleic Acid)? – Definition, Types, and Functions
Fatty Acids- Occurrence, Classification, and Examples | Essential Fatty Acids
Phospholipids- Structure, Classes and Functions
Cholesterol -Properties, Structure and Functions
Classification of Lipids | Functions Of Lipids
Metabolism of Carbohydrates | Pathways Of Carbohydrate Metabolism
Amino Acid-General structure and Classification
Coordination and Control
How does the immune system distinguish between self and non-self?
Synaptic Inhibition-Definition, Types, and Function
Are Electrical Synapses Bidirectional?
How To Measure Strength of Electrical Synapse?
Why Are Chemical Synapses More Common?
Why Chemical Synapse Is Unidirectional?
Chemical Synapse-Steps, Types, Examples, and Functions
5 Types of Synapse-An Overview
Electrical Synapse-Steps, Types, Examples, Functions, and Advantages
When Transmission Occurs at a Synapse?
Which Sensory Pathway Is Only One That Does Not Synapse In Thalamus?
Gonadal Hormones and Their Functions
Nervous Tissues-Characteristics, Types, And Functions
Learning Behavior, Definition and Types-Ecology
What is Animal Behavior?-Definition and Types
Action Membrane Potential of Neuron | Changing
Peripheral Nervous System-Definition, Composition and Types
Adrenal Glands-Hormones and Abnormalities
What are Gonads?-Definition and Types
What Is Terrestrial Locomotion in Invertebrates?
Lobes of the Brain-What Do They Control?
Difference Between Cerebellum And Cerebrum
The Spinal Cord-Structure, Working Mechanism, and Functions
What are Cytokinins?-Importance, Structure, and Functions
Evolution of Nervous System of vertebrates
What is Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis)?
What is Thyroid Gland?-Definition and Their Evolution
Sense of Smell or Olfaction-Mechanism Of Detection Of Smell
Anatomy of Human Brain-Parts and Functions
Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)-Composition, Characteristics, and Functions
Optic Nerve (CN II) | Working Mechanism and Sub-divisions
What is Abscisic Acid?-Definition, Structure and Functions
What Are Cranial Nerves?-Definition, Location, Types and Functions
What Are Auxins?-Discovery, Structure, and Functions
Brassinosteroids (BR) – Structure, Biosynthesis, and Functions
Gibberellin (GA) – Discovery, Structures, and Applications
Plant Hormones (Phytohormones) – Types and Functions
Introduction to Cell Signaling (Cellular Signaling)
Types of Hormones With Examples
Factors Affecting The Speed Of Nerve Impulse
What is Synapse? – Parts, Types, and Mechanism
What are Glands? Types and Functions
Feedback Mechanism Of Hormones- Positive and Negative Feedback
What are Hormones? Biochemistry, Classification, Types and Examples
What is Neuron? – Definition, Properties, Structure, and Type
Transport
What Are Vascular Tissues?-Composition, Types, And Functions
Difference Between Arteries And Veins
Lymphatic System-Components And Functions
Difference Between Open And Closed Blood Circulatory System
Factors Affecting The Rate Of Transpiration
What is the Immune System?-Definition and Composition
Opening And Closing Of Stomata
Human Heart-Structure, Chambers, and Function
The Cohesion Tension Theory-Definition, Processes and Mechanism
What is Stomata?-Structure, Position, and Distribution of Stomata
What is Transpiration?-Demonstration and Types of Transpiration
What is Xylem?-Components and Types
What is Phloem?-Components and Types
What Are The Transport Systems In Invertebrates?
What are White Blood Cells (Leukocytes)?-Definition, Composition, and Types
What is the Countercurrent Exchange Mechanism?
What is Immunity? | Active and Passive Immunity
What are Veins?-Structure, Types and Functions
What are Capillaries?-Types, Mechanism of Action, and Functions
Blood Coagulation-Mechanism and Process Pathways
What is Osmosis and How Does it Occur?
Arteries-Composition, Types, And Processes in Arteries
What is Plasma?-Features and its Composition
T Lymphocytes (T Cells)-Types and Function
What are Lymphocytes? – T cells, B cells, and Natural Killing Cells
Phagocytosis and Phagocytes – Discovery and Types
Hemoglobin- Structure, Types, and Functions
Blood Vessels – Definition, Types, Functions, and Disorders
B-Lymphocytes (B-Cells) – How They Develop And Function
Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes)- Composition, Shape and Function
Chromosomes and DNA
Homologous Chromosome (Structure & Functions in Different Organisms)
What is Sex Determination?-Sex Chromosomes and Sex Determining Genes
What Is Central Dogma?-Definition and Steps
Transcription-Synthesis of RNA | DNA Transcription
Genetic Code-Definition, Composition, and Characteristics
Synthesis of Protein | Translation of mRNA
Discovery of DNA As Hereditary Material
Mutations- Definition, Types, and Examples
Variation & Genetics
Cell–Unit of life
Plant Cell-Definition and Structure
Introduction To Animal Cells-Types and Composition
What are Centrosomes?-Structure and Functions
Difference Between Cell Wall And Cell Membrane
What is Protoplasm?-Composition and Types
What is Organelle? -Types and Functions
Vacuoles and Vesicles – Definition, Structure, and Functions
Prokaryotic Cell-Characteristics, Structure, and Examples
Eukaryotic Cell – Characteristics and Cell Structure
What Are Multicellular Organisms? – Characteristics and Organization
What are Unicellular Organisms? – Classification, Types, and Examples
Mesosome- Occurrence, Structure, and Functions
What are Plastids? -Definition and Types | Structure of Chloroplast
Mitochondria- Structure, Enzymes and Functions
Lysosome- Discovery and Formation of Lysosome
Evolution of Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
Cytoskeleton | Microtubules, Intermediate filament, and Microfilaments
Ribosome- Definition, Structure, Types and Functions of Ribosomes
Nucleus- Definition, Structure and Functions Of Nucleus
Why is Diffusion Faster in Small Cells?
Why is Diffusion Faster in Hot Water?
Why is Diffusion Faster in Liquids than Solids?
Why is Diffusion Faster in Lungs?
Why is Diffusion Faster in Air Than Water?
Why is Diffusion Faster in Gases?
Why Is Diffusion Faster In Water Than in Agar?
How Does Temperature Affect Diffusion In Biology?
How Does Molecular Weight Affect Diffusion?
Which Eukaryotic Cell Cycle Event Is Missing In Binary Fission?
Is A Cell Membrane Prokaryotic Or Eukaryotic?
Where Is DNA Found In Eukaryotic Cells?
What is Diffusion? (Types, Examples, And Factors)
Nutrition
Role Of The Liver In Digestion
Digestion In Hydra-Definition and Process
What is Nutrition in Plants?-Autotrophic Nutrition In Plants
Heterotrophic And Special Mode Of Nutrition In The Plants
Insectivorous Plants-Nutrition In Insectivorous Plants
What is Digestion?-Definition, Characteristics, and Types
Animal Strategies For Getting And Using Food
Stomach-Composition and Mechanism of Digestion in Stomach
Small Intestine-Definition, Structure, And Parts
Chemosynthesis-Definition, Process, and Examples
Peristalsis- Definition, Types and Mechanism
Gastrointestinal Motility and Its Control
Ecosystem
What is Deforestation?-Definition and Effects on Ecosystem
What is Population?-Characteristics and Types
Flow Of Energy In The Food Chain Of An Ecosystem
What is the Nitrogen Cycle?-Stages Of The Nitrogen Cycle
Biotic and Abiotic Components of an Ecosystem
Why is carbon important to life? An in-depth review
Why is some energy unusable by living organisms?
How Many Trophic Levels Are There In Food Web?
Population Density (Formula, Types, and Factors)
Are Humans At The Top Of The Food Chain?
Where Are Decomposers In Food Chain?
Long Food Chain (Examples and Advantages)
Short Food Chain-Example and Advantages
Why Flow Of Energy Is Unidirectional In Food Chain?
Why Food Chain Always Begin With a Producer?
How Food chain Affect Environment?
How Food Chain and Food Web are Interlinked?
What is Biome? (Definition, Types, Examples and Importance)
Food Chain (Definition, Types, and Examples)
Trophic Levels In An Ecosystem | Ecological Pyramid
What are species in Biology?-Definition, and Examples
What Is Biosphere? (Components, Types, Examples, and Importance)
Major Ecosystems
Freshwater Ecosystem (Lakes Ecosystem)-Habitats and Zones
What Is An Aquatic Ecosystem?-Features, Classification, And Productivity
What is an Ecosystem?-Components and Levels
What is Desert Ecosystem?-Location and Adaptation in Animals and Plants
What are Grasslands Ecosystem?-Definition, Types, And Human Impact
Marine Ecosystem | Importance Of The Marine Ecosystem
Most endangered biomes, and why they’re disappearing
7 Reasons Why Are Some Biomes More Fragile Than Others?
What factors primarily determine a biome?
How Do Biomes Change Over Time?
Tropical Rainforest Biome-Characteristics, Types, Location, Climate, and Examples
Tundra Biome-Characteristics, Types, Location, Climate, and Examples
Tundra Animals-Scientific Name, Habitat, and Pictures
Biotic and Abiotic Factors of Tundra Ecosystem
Savanna Biome-Characteristics, Types, Location, Climate, and Examples
Temperate Deciduous Forest Biome-Characteristics, Types, Climate, and Examples
Chaparral Biome-Characteristics, Types, Location, Climate, and Examples
Taiga Biome-Characteristics, Location, Climate, Temperature, and Examples
Desert Biome-Characteristics, Types, Location, Climate, and Examples
Desert Plants-Scientific Name, Habitats
Examples of Desert Animals-Scientific Name, Habitat
10 Examples Of Desert Ecosystem
Examples of Decomposers in Desert Ecosystem
Biotic And Abiotic Factors Of Desert Ecosystem
Threats To The Desert Ecosystem
How Desert Ecosystem Can Be Conserved?
Is Desert A Natural Ecosystem?
Tundra Ecosystem-Types and Human Impact
Biotic Factors In Aquatic Ecosystem
Man and His Environment
What is Greenhouse Effect?-Definition, Causes, And Effects
Difference Between Deforestation, Reforestation, and Afforestation
Degradation And Depletion Of Resources
What is Air Pollution?-Definition, Types, and Effects
What is Pollution?-Types and Its Impact on Ecosystem
Renewable Resources and Their Importance in Biological Systems
Examples in Biology
12 Examples of Hydrophobic Substances
10 Examples of Facultative Anaerobes
5 Examples of Biological Magnification
10 Examples of Gene Expression
15 Examples of Genetic Disorders
10 Examples of Vectors In Biology
10 Examples of Artificial Selection
10 Examples of Connective Tissue
7 Examples of Ecological Niche in Biology
10 Examples of Compounds That Make up Your Body
50 Examples of Chromosomes in Different Living Organisms
38 Examples of Viruses & Diseases They Cause
10 Examples Of Allopatric Speciation
15 Examples of Biotic factors in an Ecosystem
25 Examples of Abiotic Factors in Ecosystem
15 Examples of Adaptation in Biology
5 Examples of Deductive Reasoning in Biological Method
5 Examples of Inductive Reasoning in Biological Method
10 Examples of Natural Selection in Animals
5 Examples of Natural Selection in Microbes
5 Examples of Natural Selection in Plants
5 Examples of Natural Selection in Human
25 Examples of Enzymes & Their Functions
13 Examples of Recessive Traits
11 Examples of Dominant Traits
20 Examples of Viviparous Animals
20 Examples of Unicellular Organisms
Examples of Morphological Changes in Biology
10 Examples of Endothermic Animals
50 Examples of Animals with Chromosome Number
Examples of Competition in Biology
20 Examples of Multicellular Organisms
Examples of Chemotactic Movement in Animals and Plants
Examples of Thermotactic Movement in Animals and Plants
6 Examples of Negative Tropism
10 Examples of Neurotransmitters
Related FAQs
What do we study in biology?
Biology is the scientific study of life. It deals with the study of all types of living organisms whether they are microscopic or macroscopic(can be seen through an unaided eye).
What is the three division of biology?
There are three divisions of biology
Zoology
Botany
Microbiology
Is biology easy?
Biology is not as difficult to learn as you think, but it can be challenging to understand biological systems and processes.
A student’s knowledge of biology is most effectively acquired by mastering basic principles and concepts first before moving on to more advanced topics.
Who is the father of biology?
Aristotle is called the Father of biology. While Charles Darwin is known as the Father of Modern Biology.
What is the importance of biology?
The study of biology is related to the study of life. Understanding the living world helps us understand how species function, evolve, and interact. The quality of life has improved as a result of advances in medicine, agriculture, and many other areas.
Do you need math in biology?
There are a lot of different fields in biology. A biologist needs basic knowledge of chemistry, physics, math, and statistics for calculation and database formation. Math is used to analyze data from experiments performed by scientists.
What jobs can biology get you?
You can join the following department as a professional after getting a degree in biology:
Medicine
Surgery
Fisheries
Ecologist
Pharmaceutical
Forestry
Farming
Is a biologist a doctor?
A clinical biologist is a health professional that specializes in clinical biology, a medical specialty that is derived from clinical pathology. The concept is all about biology and assisted reproductive technology.
What is modern biology?
Modern biology has many specialized areas that study the structure, function, growth, distribution, evolution or other features of living organisms.


